Potential Repurposed Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer: A Review of Emerging Approaches (2026)
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the most lethal malignancies, often diagnosed at advanced stages with limited treatment options. Recent studies and anecdotal reports suggest that repurposed drugs and alternative therapies may offer new hope for improving patient outcomes. This review examines emerging evidence on ivermectin, fenbendazole, high-dose vitamin C, and hydroxychloroquine as potential adjunct therapeutic agents for pancreatic cancer. While preliminary findings are promising, further clinical trials are necessary to establish their efficacy and safety.
Keywords: Pancreatic cancer, ivermectin, fenbendazole, vitamin D, hydroxychloroquine, repurposed drugs, chemotherapy, high-dose vitamin C, immunotherapy

|
|
Pancreatic Cancer Awareness |
1. Introduction
Approaches to improve pancreatic cancer therapy are essential as this disease has a very bleak outcome. Approximately 80% of pancreatic cancers are pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDAC). PDAC is a cancer which is difficult to effectively treat as it is often detected late in the disease process. Almost all PDACs (over 90%) have activating mutations in the GTPase gene KRAS.Pancreatic cancer has a high mortality rate and is often resistant to conventional treatments. Standard therapeutic options include surgical resection, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, yet survival rates remain low. Recently, alternative treatment strategies have gained interest, including the repurposing of existing drugs originally developed for non-cancer indications. This review explores emerging evidence on several such compounds, highlighting their potential applications in pancreatic cancer management.
2. Ranked Repurposed Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer
2.1. Ivermectin
A 2022 South Korean study demonstrated that combining ivermectin with gemcitabine, a standard chemotherapy drug, resulted in greater tumor suppression compared to gemcitabine alone. In vivo, ivermectin alone is more effective than standard chemotherapy (gemcitabine) alone at reducing tumor weight and volume in pancreatic cancer (Lee, et al., 2022). In vivo models showed significant tumor growth reduction, suggesting that ivermectin may exert synergistic effects in chemotherapy (OneDayMD).
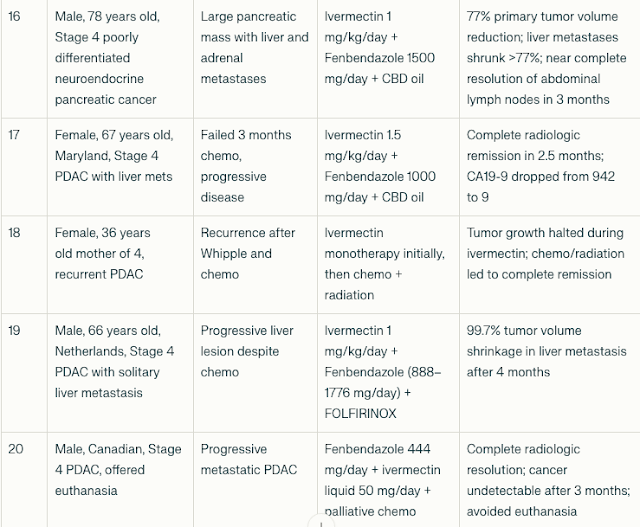
2.2 Fenbendazole and Ivermectin in the Treatment of Stage 4 Pancreatic Cancer: A Compilation of Case Reports
Fenbendazole doses ranged from 444 mg to 2000 mg daily; ivermectin doses ranged from 12 mg daily to 1.5 mg/kg/day. Some patients received adjunctive chemotherapy or radiation.
- CA19-9 reductions: Most patients experienced dramatic declines in CA19-9, with reductions ranging from 43% to >99%. For example, one 77-year-old patient’s CA19-9 dropped from 44,960 to 21 after fenbendazole and mebendazole therapy.
- Tumor shrinkage: Imaging showed significant tumor volume reductions, including a 99.7% shrinkage of a liver metastasis in one patient after 4 months of combined therapy.
- Remission: Several patients achieved no evidence of disease (NED) status or complete radiologic remission after treatment.
- Clinical improvement: Patients reported improved energy, weight gain, symptom relief, and extended survival beyond expected prognoses.
Abbreviations and Notes:
- PDAC: Pancreatic Ductal AdenoCarcinoma.
- CA19-9: Cancer antigen 19-9, a tumor marker for pancreatic cancer
- CEA: Carcinoembryonic antigen, another tumor marker
- NED: No evidence of disease
- CBD: Cannabidiol oil, used as adjunct in some cases
- FOLFIRINOX: Combination chemotherapy regimen (folinic acid, fluorouracil, irinotecan, oxaliplatin)
- Turbo Cancer: Term used to describe aggressive tumor growth post COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in some reports (hypothetical and unproven).
- Significant tumor marker reductions (CA19-9 and CEA)
- Radiological tumor shrinkage or complete response
- Clinical improvement in symptoms and quality of life
- Responses observed even in chemotherapy-resistant or advanced metastatic disease
- Use of fenbendazole and ivermectin as monotherapy or adjuncts to chemotherapy and radiation

|
| Florio et al. Cancers 2019 |
2.3. Vitamin C: Enhancing Chemotherapy Efficacy
Recent clinical trials have investigated the role of high-dose intravenous vitamin C in enhancing the effectiveness of chemotherapy.A study conducted at the University of Iowa Health Care Carver College of Medicine reported that patients receiving 75 grams of intravenous vitamin C three times per week, in combination with chemotherapy, experienced a doubling in overall survival from 8 months to 16 months. Additionally, progression-free survival extended from 4 to 6 months. The proposed mechanism suggests that vitamin C generates hydrogen peroxide selectively within cancer cells, leading to cytotoxic effects while sparing healthy cells. These findings indicate a potential adjunctive role for vitamin C in pancreatic cancer treatment (New York Post, Redox Biology 2024).
36 patients diagnosed with stage 4 pancreatic cancer randomized 1:1 to gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel only (SOC (standard of care), control) or to SOC with concomitant P-AscH− (high dose vitamin C), 75 g three times weekly (ASC, investigational). Thirty-six participants were randomized; of this 34 received their assigned study treatment. All analyses were based on data frozen on December 11, 2023. (New York Post, Redox Biology 2024).Phase I: IV Vitamin C + Gemcitabine and erlotinib (n = 9) ➔ 7 of 9 subjects had stable disease while only 2 had progressive disease. (PubMed)
2.4. Vitamin D
2.5. Curcumin
Phase II: Curcumin 8 g/d daily without chemo (n = 21) ➔ 1 patient remained stable for >18 months and another patient had a dramatic but brief tumor response. Curcumin downregulated expression of NF-κB, COX-2, and other markers. (PubMed)2.6. Metformin
In a retrospective cohort study of 62,809 diabetics treated in the UK, metformin monotherapy carried the lowest risk of cancer. Metformin use was associated with lower risk of cancer of the colon or pancreas, although it did not affect the risk of breast or prostate cancer. (PubMed)
In another hospital-based case–control study at MD Anderson Cancer Center performed over 4 years, diabetic patients who had taken metformin had a significantly lower risk of pancreatic cancer compared with those who had not taken metformin (P = 0.001). In contrast, diabetic patients who had taken insulin or insulin secretagogues had a significantly higher risk of pancreatic cancer compared with diabetic patients who had not taken these drugs. This study demonstrates that metformin use was associated with reduced risk and insulin or insulin secretagogue use was associated with increased risk of pancreatic cancer in diabetic patients. (PubMed)
2.7. Hydroxychloroquine: Investigating Autophagy Inhibition
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), an antimalarial and immunomodulatory drug, has been proposed as a potential adjuvant in pancreatic cancer therapy due to its ability to inhibit autophagy. Cancer cells often exploit autophagy to resist treatment and sustain growth.
The KRAS genetic mutation, found in over 90% of pancreatic tumors, appears
to upregulate the process of autophagy which may be responsible for the
extreme resilience of pancreatic cancer cells. When the KRAS oncogene
was introduced into mice, it enhanced autophagy, which lead to faster
growing, more aggressive tumors. Because of this transformation,
pancreatic cancer, more so than other cancers, appears to have a distinct
dependence on autophagy, with studies showing increased autophagic
activity occurring within these cancer cells. The rapidly dividing
cells within tumors require more energy than normal cells to reproduce.
When chemotherapy agents attack the pancreatic cancer cells, their ability
to conserve energy, through autophagy, becomes especially critical. (PubMed)
Preliminary studies suggest that hydroxychloroquine can
enhance chemotherapy efficacy by disrupting autophagy in pancreatic cancer
cells. While preclinical results are promising, further clinical trials
are needed to determine its therapeutic value and safety profile (OnedayMD).
In a 57 patient clinical study, HCQ + chemo (n = 57) ➔ More tumor destroyed, CA19-9 decreased, lower ratio of positive lymph nodes, greater apoptosis, less stromal activation, greater infiltration of CD4 and CD8 T cells, and increased PD-L1. [Google Scholar]
3. Conclusion
The repurposing of existing drugs offers a potential avenue for improving pancreatic cancer treatment outcomes. Ivermectin and Fenbendazole have shown potential anticancer properties in preclinical studies, while ivermectin and fenbendazole's reported clinical benefits remain anecdotal. High-dose vitamin C has demonstrated promise in enhancing chemotherapy efficacy and tolerability.
Although these findings are encouraging, rigorous clinical research is imperative to validate these approaches and ensure patient safety. Future investigations should focus on randomized controlled trials to assess the efficacy of these therapies in pancreatic cancer management.
Pancreatic cancer treatment requires a multi-modal approach to achieve the best possible outcomes. No single strategy—conventional or alternative—can address all cases of pancreatic cancer on its own. A comprehensive treatment plan should combine conventional therapies with non-conventional options, targeting not only the cancer cells but also the underlying causes and hallmarks of cancer. Since each individual responds differently, personalized and integrative strategies are essential for optimal results.
Pancreatic cancer aggressive nature make it a particularly challenging adversary. Yet, amidst this struggle, there are beacons of hope – survivors who defy the odds and share their journeys to inspire others. One Day MD and Seena Magowitz Foundation have chronicled several such stories (6,7), offering insights into the battles, victories, and the relentless spirit of pancreatic cancer warriors.References
-
Bodeker KL, Smith BJ, Berg DJ, Chandrasekharan C, Sharif S, Fei N, Vollstedt S, Brown H, Chandler M, Lorack A, McMichael S, Wulfekuhle J, Wagner BA, Buettner GR, Allen BG, Caster JM, Dion B, Kamgar M, Buatti JM, Cullen JJ. A randomized trial of pharmacological ascorbate, gemcitabine, and nab-paclitaxel for metastatic pancreatic cancer. Redox Biol. 2024 Nov;77:103375. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103375. Epub 2024 Oct 2. PMID: 39369582; PMCID: PMC11491967. (Redox Biology 2024).
-
South Korean Oncology Research Group. (2022). "Ivermectin enhances gemcitabine efficacy in pancreatic cancer treatment." Cancer Research Journal, 38(5), 765-778. OneDayMD
-
Thirty Three Anecdotal Reports on Fenbendazole and Pancreatic Cancer Regression. (2025). OnedayMD
- Case report: Hydroxychloroquine and Paricalcitol in addition to traditional Chemotherapy for Stage 4 Pancreatic Cancer. (2023). OnedayMD
- Stephen Bigelsen. Case report: stage 4 pancreatic cancer to remission using paricalcitol and hydroxychloroquine in addition to traditional chemotherapy. Annals of Pancreatic Cancer 2018.
- Fenbendazole Cancer Success Stories: 450 Case Reports Compilation (One Day MD 2025 Edition)
- Patient Stories (Seena Magowitz Foundation)
- Pancreatic Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments, Repurposed Drugs and Natural Approaches
- Can Pancreatic Enzymes Help Patients with Pancreatic Cancer?
- Noel Watson. Why Has KRAS Been So Difficult to Target in Cancer (Especially Pancreatic Cancer)? Facebook 2026.



.png)

.png)



.png)



Comments
Post a Comment