Next-Generation CAR-T Cell Therapies: Longer-Lasting and Ultrasound-Activated Cells
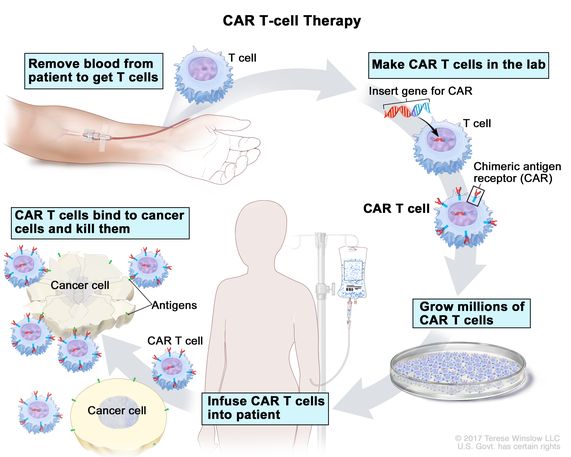
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has revolutionized treatment for blood cancers, but its application to solid tumors—like glioblastoma (brain cancer) and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC)—remains limited by poor persistence, rapid exhaustion, immunosuppressive tumor microenvironments, and off-tumor toxicity. In 2025, breakthroughs in engineering have produced next-generation CAR-T cells with enhanced longevity and precise, remote activation via focused ultrasound (FUS), offering new hope for these challenging cancers.
Enhancing Persistence: Building Longer-Lasting CAR-T CellsTraditional CAR-T cells often exhaust quickly in solid tumors due to chronic antigen stimulation and hostile conditions. Innovations focus on genetic modifications to improve survival and function:
- Positive feedback loops and advanced signaling domains: Designs incorporating synthetic circuits reprogram tumor engagement into sustained CAR expression, reducing exhaustion. Single-cell analyses show these cells maintain higher cytotoxicity over time.
- Co-stimulatory enhancements: Third- and fourth-generation CARs with domains like 4-1BB or IL-15 armor promote memory formation and prolonged activity.
- Combination strategies: Pairing with checkpoint inhibitors or cytokines (e.g., IL-12 fusion) boosts expansion and persistence in preclinical models.
- Mechanism: Cells feature an ultrasensitive heat-shock promoter (activated by mild FUS-induced heating) plus a positive feedback loop. Initial ultrasound "primes" CAR production; tumor antigen engagement then sustains it, "echoing" the signal for long-lasting activation (up to 5+ days vs. <24 hours in prior inducible systems).
- Advantages:
- Spatial control minimizes off-tumor toxicity.
- Prolonged activity overcomes exhaustion.
- Versatile: Adapted for targets like human GD2 (glioblastoma) and PSMA (prostate cancer), with strong tumor regression in mouse models without damaging healthy tissues.
- Glioblastoma: EchoBack-CAR T suppressed orthotopic GBM in mice, outperforming constitutive CARs. Combined with tumor-priming FUS, it addresses blood-brain barrier challenges.
- Pancreatic Cancer: Ongoing adaptations target dense stroma; preclinical combos (e.g., with KRAS inhibitors or oncolytic viruses) enhance infiltration. Early testing of ultrasound strategies shows promise for PDAC.
References:
- Top 10 Pharmaceutical Companies by Revenue
- Top 10 most anticipated drug launches of 2025
- Top 10 Pharma Companies by Market Cap (2025)
- Top 10 Emerging Cancer Therapies to Watch in 2025
- 22 Best Alternative Cancer Treatments 2025: Proven Interventions
- The Transformative Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics on Global Human Health: A Systematic Review and Forward-Looking Analysis
- KRAS Inhibitors: Targeting the 'Undruggable' Mutation in 2025 and Beyond
- CAR-T vs CAR-NK Therapy — and Why Metabolic Modulation May Decide the Winner (2026)
.png)

.png)






Comments
Post a Comment