18 Best Natural Treatments to Reduce Cytokine Storm, a Severe Complication from COVID-19 (October 2022)
As of October 2022, there are more than 1,700 early treatment studies that have been published and shared with the whole world. New ones are being added every day.
This is a review of the literature to date, covering multiple observational
studies, randomized controlled trials and references related to natural
supplements and cytokine storm.
It appears one of the differences between those who have a mild illness and
severe illness is related to the body's ability to reduce the hyperimmune
response that leads to a cytokine storm and the hyper-coagulability
(tendency for blood clots) that often accompanies it. The cytokine storm may
be one possible way to explain the severe reaction of those in hospitals.
This may also explain why younger people and those with a healthy immune
system and without preexisting health conditions tend to have an easier
time. Their bodies may release lower levels of cytokines creating just
enough inflammation for healing.
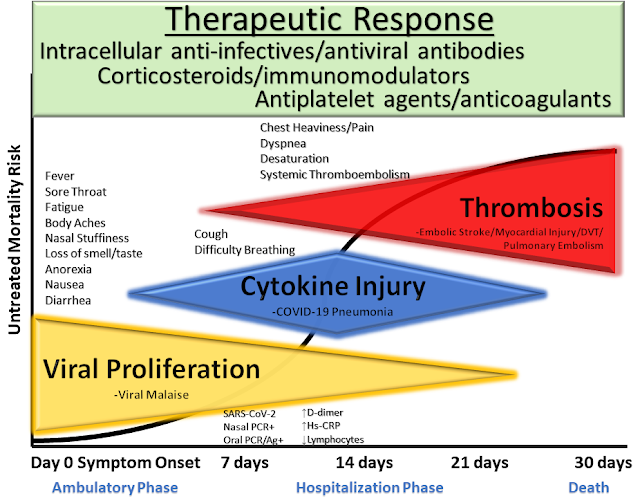
With age, immune function markedly declines which means we must take steps to support a healthy immune response. Nutritional supplements are meant to tip the scales in favour of you in terms of your immune system and to improve your probability of a smooth recovery, if at all you do get COVID-19. You will still need to follow the advice given by CDC, WHO and your local authority in terms of local guidelines such as mask wearing, social distancing, vaccination and avoiding crowds.
We know that while a large percentage of the population only experiences
mild to moderate symptoms of COVID-19 and won’t require hospitalization,
others experience severe symptoms and complications, require
hospitalization, or may even die.
Our aim here isn't to cover what the doctors will do to prevent or stop a
cytokine storm in the hospital environment. As this is a consumer-oriented
article, our aim here is to cover actionable ways for you to reduce your
risk of a cytokine storm. Do take note that supplements are not 100%
protective or curative against COVID-19. Please consult your health care
professional before using products based on this article.

McCullough et al. Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2020
With age, immune function markedly declines which means we must take steps to support a healthy immune response. Nutritional supplements are meant to tip the scales in favour of you in terms of your immune system and to improve your probability of a smooth recovery, if at all you do get COVID-19. You will still need to follow the advice given by CDC, WHO and your local authority in terms of local guidelines such as mask wearing, social distancing, vaccination and avoiding crowds.
Contents
Immune Nutrients to Calm Cytokine Storm
If you want to optimize your immune health and reduce your risk of a
cytokine storm, there are various immune nutrients and foods that may reduce cytokines.
While at this point, research is on-going and scientists are working hard to understand COVID-19 and find treatment options, these are some promising developments. The good news is that you don’t have to wait to take steps to protect your health. There are a number of things that you can do to improve your immune system, including using immune nutrients that may help to calm a cytokine storm (J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, The Lancet, Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.
While at this point, research is on-going and scientists are working hard to understand COVID-19 and find treatment options, these are some promising developments. The good news is that you don’t have to wait to take steps to protect your health. There are a number of things that you can do to improve your immune system, including using immune nutrients that may help to calm a cytokine storm (J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, The Lancet, Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.
Related: Cytokine Storm Signs and Symptoms
In all cases, the data consistently show that low vitamin D levels raises your risk of COVID while higher baseline levels and/or supplementation lowers all risks by 1.5 to three times.
“Each 10 ng/mL increase in vitamin D levels was associated with a 45 % and 26 % lower risk of 45-day mortality (HR: 0.55, 95 % CI: 0.40–0.74) and ICU mortality due to COVID-19 (HR: 0.74, 95 % CI: 0.60–0.92), respectively.”
Since the outbreak of the pandemic, many vitamin D
sufficiency studies have been conducted. Almost all of them
show that an adequate vitamin D level reduces the chance of
(a) getting ill, (b) ending up in the hospital, and (c)
dying.
Almost all studies consider a vitamin D blood serum level of >30 ng/mL ‘adequate/good’. Several studies have shown that people with a blood serum level of >50 ng/mL hardly get sick at all. Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis (Nutrients 2021) suggested that COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/ml 25(OH)D3.
Safety: Daily intakes of up to 25–100 mcg (1,000 IU–4,000 IU) vitamin D in foods and dietary supplements are
safe for children (depending on their age) and up to
100 mcg (4,000 IU) are safe for adults. These values,
however, do not apply to individuals receiving vitamin
D treatment under the care of a physician. Higher
intakes (usually from supplements) can lead to nausea,
vomiting, muscle weakness, confusion, pain, loss of
appetite, dehydration, excessive urination and thirst,
and kidney stones. In extreme cases, vitamin D
toxicity causes renal failure, calcification of soft
tissues throughout the body (including in coronary
vessels and heart valves), cardiac arrhythmias, and
even death.
Quercetin as a Zinc Ionophore
Quercetin is a zinc ionophore (J Agric Food Chem. 2014). A 2015 study found that that Quercetin shows inhibitory activity in the early stages of a wide range of influenza viruses, including H1N1 and H5N1 (Viruses 2016). Although influenza is not in the same family of viruses as the coronavirus, it’s plausible that a similar mechanism could apply here. There is actually some evidence that Quercetin has already proven effective at treating Ebola and Zika viruses.
Quercetin Dosage
The FLCCC I-MASK+ protocol recommends 250 mg daily for prevention and 250 mg twice daily for early treatment.
Precaution: Quercetin should be used with caution in
patients with hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone) and
relevant thyroid hormone levels should be monitored.
Related: Is Zinc Picolinate Elemental Zinc
There are more than 20 studies of curcumin in COVID-19 published. And the results
are promising.
Temporarily taking megadoses of vitamin C supplements to combat a case of the cold or flu is likely not going to cause a problem.
Many vitamin C supplements that are above the US RDA are
sold in the market. It’s important to seek a physician’s
advice if you intend to take high dose vitamin C on a
long term basis. To be on the safe side, you may also
request for your kidney functions to be monitored.
For long-term, daily use, your best bet is to eat a diet
that is full of high quality organic vegetables and
fruits that are minimally processed. Not only will you
get vitamin C, but you will get all the other accessory
nutrients and micronutrients that are needed to optimize
it.
Black seed oil is extracted from N. sativa seeds and has been used in traditional medicine for over 2,000 years due to its many therapeutic benefits.
Thymoquinone which is the active ingredient in N. sativa
seeds has demonstrated effects in significantly reducing
the cytokine storm chances and consequent mortalities (Source).
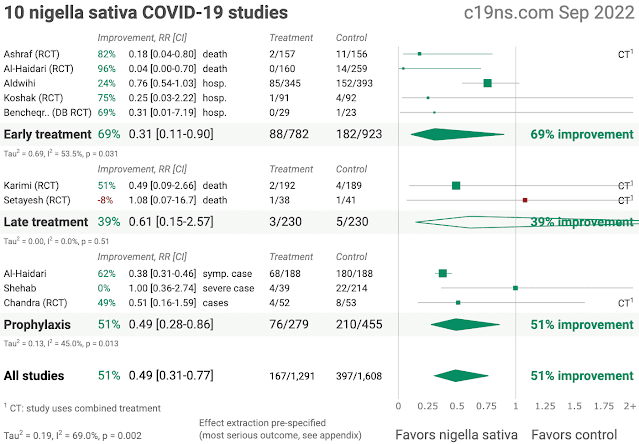
Summary results of 6 published clinical studies are available
on this dedicated webpage: c19ns.com. The 4 RCTs (Randomized Controlled Trials) provide evidence that
Nigella Sativa was associated with an average improvement of
84% in decreasing the likelihood of death and hospitalization.
Melatonin is a hormone synthesized in your pineal
gland and many other organs. While it is most
well-known as a natural sleep regulator, it also has
many other important functions. For example, melatonin
is a potent antioxidant (Antioxidants 2020) with the rare ability to enter your mitochondria,
where it helps “prevent mitochondrial impairment,
energy failure and apoptosis of mitochondria damaged
by oxidation.” It also helps recharge glutathione and glutathione deficiency has been linked to COVID-19
severity.
Much of the research on NAC has used an inhaled, liquid form of this compound. This form—which is classified as a drug, not a dietary supplement—is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a mucolytic agent and for decreasing respiratory secretion viscosity (Source). Products containing NAC are also sold as dietary supplements.
That said, NAC is a natural alternative for aspirin and an over-the-counter supplement that both
prevents blood clots and breaks up existing ones i.e.
anticoagulant effects. NAC also has other benefits that
makes it useful against COVID-19.
Safety: As an FDA-approved drug, the safety
profile of NAC has been evaluated (Source). Reported side effects of oral NAC include nausea,
vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, indigestion, and
epigastric discomfort. No safety concerns have been
reported for products labeled as dietary supplements that
contain NAC. (Source)
Epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) 200mg (prevention) or
400 mg (early treatment) 1 time a day (J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014) is part of the Zelenko protocol for prevention and early treatment of
COVID-19. EGCG acts as a zinc ionophore and
therefore needs to be combined with zinc.
The strong oxidative stress-reducing and
anti-inflammatory effects of green tea catechins,
including epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), have been
well established. A solution of green tea catechins
was found to inactivate COVID-19 virus in the
laboratory (Ref).
Other laboratory and computer models suggest tea
catechins may inhibit viral infectivity and growth (Ref). It has been proposed that EGCG, due to its
immune-modulating effect, could have a role in
suppressing hyper-inflammation and preventing lung
fibrosis in patients with severe acute viral respiratory
illness (Ref).
This protection may have come from the effect EPA and DHA have on the body. An opinion paper published in June 2020 in the journal Frontiers in Physiology expounded on how "EPA and DHA supplementation can alter many biological pathways which may have a direct influence in the outcome of COVID-19."(Front. Physiol., 19 June 2020) The writers listed the many nutrients that play a key role in managing a cytokine storm and continued:
"Among these micronutrients, LC-PUFAs (long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids) such as EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are noteworthy because of their direct influence in the immunological response to viral infections.
Among these complex immunomodulatory effects, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1ß (IL-1β)—because of the suspected central regulatory role in the "cytokine storm"—should be highlighted."
The omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and
docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) modulate inflammatory
processes in the body through a variety of mechanisms (Ref, Ref). Severe acute viral respiratory infections can
sometimes trigger cytokine storm, in which excessive
production of inflammatory cytokines leads to uncontrolled
systemic inflammation and life-threatening tissue and
organ damage. Another phenomenon, called eicosanoid storm,
has also been proposed to contribute to widespread
inflammation, tissue damage, and organ failure. Eicosanoid
storm is characterized by excessive production of
pro-inflammatory and procoagulant eicosanoids made from
arachidonic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid synthesized in the
body and obtained from dietary animal fat (Ref, Ref). By competing with arachidonic acid for metabolic
enzymes, EPA and DHA decrease the production of
pro-inflammatory and procoagulant eicosanoids and increase
production of specialized inflammation-resolving compounds
(Ref, Ref).
Accumulating evidence shows omega-3 fatty acids, administered orally or intravenously, may help control inflammation and improve outcomes in critically ill patients, including those with ARDS.489 A meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials with a total of 1,280 critically ill patients with ARDS found supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids, in combination with gamma-linolenic acid (a less-inflammatory omega-6 fatty acid) and antioxidants, improved markers of lung function; however, only hourly administration, rather than large bolus intravenous dosing, was associated with reduced mortality. Although reductions in mechanical ventilation and length of stay in intensive care were seen, these effects did not reach statistical significance (Ref).
An observational study in 100 patients hospitalized with a severe acute viral respiratory illness found higher levels of EPA plus DHA were associated with lower mortality, though the effect was not statistically significant, possibly due to the small number of participants (Ref). During an outbreak of a severe viral respiratory infection, another study found countries with the highest intake of omega-3 fatty acids from marine sources had lower mortality rates than other regions of the world (Ref). The same research group used computer modeling to show how omega-3 fatty acids might bind to the highly infectious virus and interfere with its ability to enter cells (Ref).
EPA and DHA have a direct influence in the immunological response to viral infections and can modulate immune response and function.
Animal-based omega-3 fats, especially DHA, also help prevent thrombosis (a blood clot within a blood vessel) by decreasing platelet aggregation. Hypercoagulation is another complication of severe COVID-19 infection that can have lethal consequences.
Omega-3 also lowers your risk of lung dysfunction, protects against lung damage and secondary bacterial infections, and improves mitochondrial function.
Research shows that by lowering triglycerides, the risk of developing a cytokine storm is diminished. Omega-3 supplementation is known to lower triglycerides, but krill oil does so more effectively than fish oil.
An interesting development published in Science, Nov 2020 revealed that linoleic acid (omega-6) binds with
the 'spike protein' of the COVID-19 virus and interferes
with the entrance of the virus into a human cell via the
ACE-2 receptors. The study also revealed that in
human cells, Linoleic Acid supplementation synergizes with
the COVID-19 drug remdesivir in suppressing SARS-CoV-2
replication.
A paper, published in BMJ Open Gastroenterology in
April 2022 by Dr. Sabine Hazan, concluded that the following were protective against
severe COVID-19 infection:
Lactoferrin is an iron-binding protein made by cells
such as those in secretory glands and activated
neutrophils (a type of immune cell). It is found in
most bodily fluids, including tears and breast milk,
and lactoferrin derived from bovine whey is frequently
used in supplements (Ref). Lactoferrin is an immune modulator, capable of
enhancing antimicrobial immune activity while reducing
inflammation, and has exhibited a broad spectrum of
activity against bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and
viruses (Ref). Laboratory research also suggested lactoferrin may
inhibit entry of a highly infectious respiratory virus
into cells by blocking its interactions with cell
membrane components (Ref).
Lactoferrin may slow pathogen multiplication through its iron binding capacity. While iron is required for DNA replication and energy production, the presence of excess iron increases free radical generation, stimulates inflammatory processes, and exacerbates viral infection by promoting increased viral replication (Ref). Furthermore, patients with a severe acute viral respiratory infection have been found to have elevated levels of ferritin, and these levels correlated with increased risk of death (Ref). In its iron-free state (apolactoferrin), lactoferrin can sequester pro-oxidant free iron, lowering oxidative stress and suppressing the growth of pathogens, and possibly mitigating the serious complications of infection (Ref).
In a pilot trial, 75 patients who tested positive for an acute viral respiratory tract infection were treated at home with a liposomal preparation of a combination of 32 mg bovine lactoferrin with 12 mg vitamin C, with or without 10 mg liposomal zinc, four to six times daily for 10 days. In addition, lactoferrin nasal drops, mouth spray, and aerosol were used as needed by participants with headaches, loss of sense of smell and taste, nasal congestion, dry cough, or difficulty breathing. After 48 hours, all symptoms had diminished except loss of smell and taste, and by day five, all infected participants recovered from their illness with only loss of smell and taste remaining as residual symptoms (Ref).
The soil concentration of selenium varies geographically around the world, affecting selenium status and resulting in endemic insufficiency and deficiency (Ref). A study comparing COVID-19 survival to regional selenium status during a major outbreak in China found survival was more likely in high-selenium regions (Ref). A study done during an outbreak in Germany found higher selenium and selenium-containing protein levels in COVID-19 infection survivors versus non-survivors (Ref).
Blood selenium levels have been noted to diminish in patients with critical illness, and lower levels are correlated with more severe illness and lower chance of survival (Ref). A meta-analysis of 19 randomized controlled trials found intravenous selenium supplementation in critically ill patients reduced total mortality (but not 28-day mortality) and shortened the length of hospital (but not intensive care unit) stay (Ref).
As explained in this paper, astaxanthin has a very unique molecular structure that allows it to penetrate the bilayer membrane of cells. The ability to quench reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals in both the inner and outer layers of the cellular membrane allows it to provide superior protection against oxidative stress, compared to other antioxidants.
Vitamin E and beta-carotene, for example, only work in the inner side of the membrane, and vitamin C only works on the outer side.
In short, astaxanthin ticks many important boxes when it comes to ameliorating COVID-19, including immune response regulation and the enhancement of both cell-mediated and humoral immune responses, as well as the simultaneous protection against oxidative damage and inflammation.
1. Vitamin D3 and Cytokine Storm
At this point, there is simply no question that vitamin D optimization is a crucial component of COVID-19
prevention and treatment. In addition to the many studies
published during 2020 and 2021, since December 2021, four
large systematic meta-analyses (R, R, R, R) have been published, looking at either vitamin D levels,
supplementation or both.
In all cases, the data consistently show that low vitamin D levels raises your risk of COVID while higher baseline levels and/or supplementation lowers all risks by 1.5 to three times.
Vitamin D, as an immuno-modulator, is a perfect
candidate for countering the immune dysregulation common
with COVID-19. Vitamin D deficiency affects the body’s
susceptibility to infection and has been associated with
influenza, hepatitis C, human immunodeficiency virus
(HIV) and other viral diseases [Source]. Surveys indicate that most people in the
United States consume less than recommended amounts of
vitamin D. Sun exposure, which increases serum 25(OH)D
levels, is one of the reasons serum 25(OH)D levels are
usually higher than would be predicted on the basis of
dietary vitamin D intakes alone. Vitamin D deficiency is
also known to enhance a process known as the “cytokine
storm” (Marik 2020).
According to a July 2022 paper:
“Each 10 ng/mL increase in vitamin D levels was associated with a 45 % and 26 % lower risk of 45-day mortality (HR: 0.55, 95 % CI: 0.40–0.74) and ICU mortality due to COVID-19 (HR: 0.74, 95 % CI: 0.60–0.92), respectively.”
Almost all studies consider a vitamin D blood serum level of >30 ng/mL ‘adequate/good’. Several studies have shown that people with a blood serum level of >50 ng/mL hardly get sick at all. Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis (Nutrients 2021) suggested that COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/ml 25(OH)D3.
In a June 2022 review paper titled “The Role of Diet and Supplements in the Prevention and
Progression of COVID-19: Current Knowledge and Open
Issues” published in the journal Preventive Nutrition and Food
Science, researchers said:
"The consumption of vitamin C and D supplements, in
addition to a healthy diet, could be promoted as a
co-adjuvant therapy for COVID-19..."
For more evidence, check out the evidence tracker
on vitamin D and COVID-19 from c19vitamind.com (constantly updated), with more than 80
published treatment studies and more than 120
sufficiency studies by more than 900 scientists.
Vitamin D has also been shown to have
an anticoagulant effect. A decrease
in 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] concentration has
also been associated with an increased risk of
venous thromboembolism (PubMed).
Vitamin D and Omicron
Will Vitamin D Work Against Omicron BA4 and BA 5?
Vitamin D is not variant specific because it's primary
mode of action is to support the body’s immune system
which reacts in a variety of ways against viral
attack, not just in a specific antibody reaction to a
specific spike protein.
Vitamin D, Resveratrol and Cytomegalovirus
Dormant cytomegalovirus (CMV) is carried by 70-90% of the adult population and is
reactivated by inflammation. One third of patients in hospital intensive care
units reactivate CMV which doubles their mortality
rate. There is agreement that Covid-19 co-infection with cytomegalovirus is
associated with higher rates of mortality in older
people who have an aged (senescent) immune system.
Cytomegalovirus also dulls the vitamin D
receptors thus preventing the active form of vitamin D to
enter living cells.
Resveratrol inhibits replication of cytomegalovirus
in infected lung cells. Resveratrol also binds to and activates the vitamin
D receptors, thus allowing cells in the body to respond to
vitamin D.
Related: Best Vitamin D Supplement
2. Quercetin
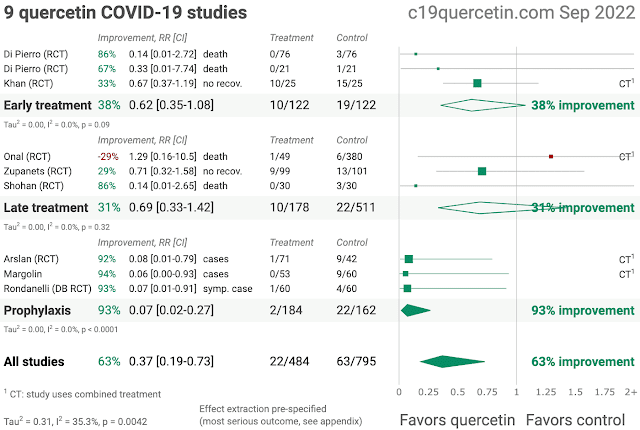
As of September 2022, there have been 9 published studies of
quercetin and COVID-19 (c19quercetin.com).
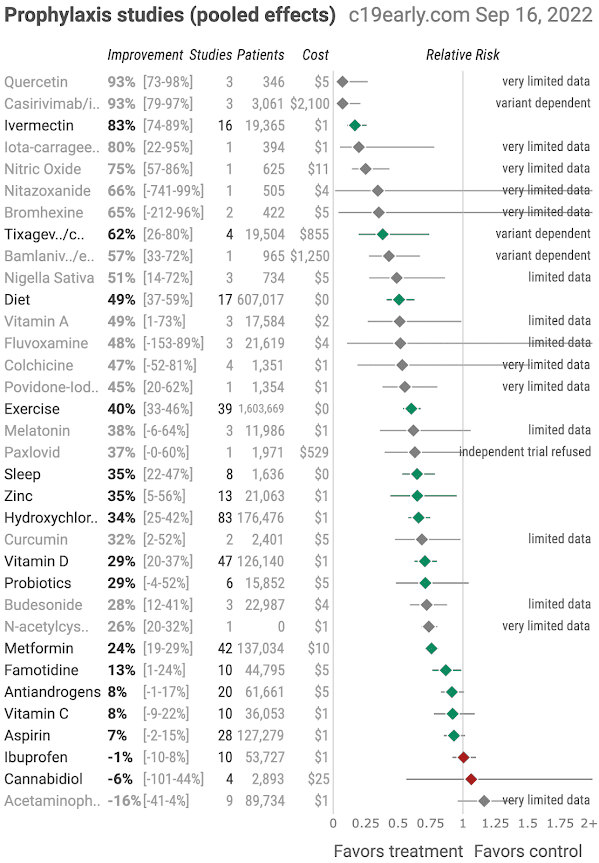
Quercetin is also no. 1 in this prevention studies league
table:
Quercetin is a pigment that is found in plants, vegetables, and
fruits, and serves as an immune nutrient offering many
health benefits. Elderberry, red onions, white onions and
cranberries are the richest sources of quercetin. It is a
flavonoid and antioxidant that may help to reduce
inflammatory cytokines, infections, allergies and anti-blood clot property. Research has found that quercetin may be particularly
beneficial for viral respiratory infections.
Quercetin as a Zinc Ionophore
Quercetin is a zinc ionophore (J Agric Food Chem. 2014). A 2015 study found that that Quercetin shows inhibitory activity in the early stages of a wide range of influenza viruses, including H1N1 and H5N1 (Viruses 2016). Although influenza is not in the same family of viruses as the coronavirus, it’s plausible that a similar mechanism could apply here. There is actually some evidence that Quercetin has already proven effective at treating Ebola and Zika viruses.
Quercetin and Vitamin C
Incidentally, ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and the
bioflavonoid quercetin (originally labeled vitamin P)
were both discovered by the same scientist — Nobel prize
winner Albert Szent-Györgyi. Quercetin and vitamin C also act as an antiviral
drug, effectively inactivating viruses.
Quercetin Dosage
The FLCCC I-MASK+ protocol recommends 250 mg daily for prevention and 250 mg twice daily for early treatment.
Quercetin works best when taken with vitamin
C and Bromelain, as vitamin C helps activate it and
bromelain helps with the absorption.
Quercetin and ivermectin interactions? According
to Drugs.com: "No interactions were found between ivermectin
and Quercetin. This does not necessarily mean no
interactions exist. Always consult your healthcare
provider."
Note: Some physicians are recommending this supplement to
reduce viral illnesses because quercetin acts as a zinc
ionophore to improve zinc uptake into cells. It is much less
potent than HCQ (hydroxychloroquine) as a zinc transporter,
and it does not reach high concentrations in lung cells that
HCQ does. Quercetin may help reduce risk of viral illness if
you are basically healthy. But it is not potent enough to
replace HCQ for treatment of COVID once you have symptoms,
and it does not adequately get into lung tissue unless you
take massive doses (3-5 grams a day), which cause
significant GI (gastrointestinal) side effects such as
diarrhea.
Related: Best Quercetin Zinc Supplement
3. Zinc and Cytokine Storm
Zinc deficiency can significantly impact your immune
system, but it can also result in a hyper inflammatory
response from pro-inflammatory cytokines (Nutrients. 2017).
As early as 2010, zinc has been shown in a lab study to
inhibit regular coronavirus (not the current SARS-CoV-2)
in a 2010 publication.
Yet another study from Belgium (Nutrients 2021) has demonstrated the
significance and importance of adequate levels of zinc
and selenium in patients who have COVID-19, and
especially in those who have underlined comorbidities
identified to increase the severity of disease.
Check out the evidence tracker on zinc and COVID-19
from c19zinc.com (constantly updated).
Zinc is another powerful immune nutrient known for
its benefits for providing immune health support and
inflammation reduction as well as for improving cold
and respiratory symptoms, wound healing, acne
reduction, and lowering the risk of age-related
diseases. This trace element is essential to to cell
function and involved in over 100 enzymes. Research
on atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus suggests
that zinc deficiency may contribute to low-grade
systemic inflammation.
Aging is associated with compromised immunity, that
just means that your immune response to pathogens
and infections starts to slow and is less robust,
including a reduced vaccine immune
response/efficacy.
Improving zinc intake/zinc status improves/modulates/enhances immune function. The flip side is, while some aspects of immunity slow, others increase. Uncontrolled immune responses drive excess inflammation. Zinc helps to balance all of this.
Improving zinc intake/zinc status improves/modulates/enhances immune function. The flip side is, while some aspects of immunity slow, others increase. Uncontrolled immune responses drive excess inflammation. Zinc helps to balance all of this.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) states:
“Zinc is involved in numerous aspects of cellular metabolism. It is required for the catalytic activity of approximately 100 enzymes and it plays a role in immune function, protein synthesis, wound healing, DNA synthesis, and cell division. Zinc also supports normal growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence and is required for proper sense of taste and smell.”
“Zinc is involved in numerous aspects of cellular metabolism. It is required for the catalytic activity of approximately 100 enzymes and it plays a role in immune function, protein synthesis, wound healing, DNA synthesis, and cell division. Zinc also supports normal growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence and is required for proper sense of taste and smell.”
Zinc and COVID-19
Foods that are high in zinc include oysters, crab,
lobster, mussels, red meat, and poultry. Cereals are
often fortified with zinc. Most multivitamin and
nutritional supplements contain zinc.
Excessive doses may interfere with copper absorption, which could negatively affect your immune system as it can cause copper deficiencies, blood disorders and potentially permanent nerve damage. Zinc can also impair the absorption of antibiotics, and use of zinc nasal gels or swabs has been linked to temporary or permanent loss of smell.
Safety: Taking zinc long term is
typically safe for healthy adults, as long as the
daily dose is under the set upper limit of 40 mg of
elemental zinc (PubMed). Be aware that typical daily doses of zinc
provided by zinc lozenges generally exceed tolerable
upper limits for zinc, and for this reason,
they should not be used for longer than about a
week.
Excessive doses may interfere with copper absorption, which could negatively affect your immune system as it can cause copper deficiencies, blood disorders and potentially permanent nerve damage. Zinc can also impair the absorption of antibiotics, and use of zinc nasal gels or swabs has been linked to temporary or permanent loss of smell.
Zinc Form and Dosage
There are several types of zinc supplements. Supplements contain several forms of zinc, including zinc gluconate, zinc citrate and zinc picolinate. The percentage of elemental zinc varies by form. To find out the percentage of elemental zinc in each form, check out elemental zinc percentage.
Chelated zinc is a general form of supplementary
zinc in which the zinc is chelated — or bound — to
a compound to make it easier for the body to
absorb. Zinc picolinate or zinc gluconate are
formed when zinc is chelated to picolinic acid or
gluconic acid, so the main difference between zinc
gluconate and picolinate is what compound it is
bound to.
There are several types of zinc supplements. Supplements contain several forms of zinc, including zinc gluconate, zinc citrate and zinc picolinate. The percentage of elemental zinc varies by form. To find out the percentage of elemental zinc in each form, check out elemental zinc percentage.
To find out which zinc supplement to consider,
check out best zinc supplement.
Most people do not lack an intake of zinc, but
in disease state, there might be an increase in
demand by the body. The FLCCC I-MASK+ protocol recommends 30 mg a day for
prevention and 100 mg a day for early treatment
of COVID-19. This should not be taken long term
without evaluation of your zinc/copper ratios.
The ideal dose for prevention while the COVID-19
risk is high is 40-100 mg/d, a portion of which
comes from zinc lozenges to spread the zinc
through the tissues of the nose, mouth and throat.
It should be accompanied by at least 1 mg copper
from food and supplements for every 15 mg zinc.
Do take note that you should keep the dosage
back to within 40 mg/d once the exposure risk is
back to normal.
4. Curcumin and Turmeric
Can Turmeric Supplements Reduce Cytokine Storm? Curcumin, a yellow carotenoid from turmeric, is well known for its anti-inflammatory and free radical-scavenging effects.Curcumin and COVID-19
Curcumin also acts as natural zinc ionophores and can
promote the cellular uptake of zinc and can be used with
zinc to increase the effectiveness of these compounds in
the inhibition of the virus (Ref).
It has also demonstrated antiviral effects against a
range of respiratory viruses, including influenza A
virus and others (Ref). Computer models suggest curcumin may interfere
with viral entry into cells as well as viral
replication inside cells (Ref).
Numerous preclinical studies indicate curcumin may
activate antiviral immunity; at the same time,
curcumin appears to inhibit infection-induced
inflammatory signaling and promote anti-inflammatory
processes, reducing the potential for a cytokine
storm and ARDS and protecting other organ systems
(Ref). By suppressing inflammation, curcumin has the
potential to help mitigate complications and
sequelae of severe acute viral respiratory
infections (Ref).
Curcumin has been demonstrated (Ref) to suppress several inflammatory cytokines and
mediators of their release such as tumor necrosis
factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), IL-1, IL-8 and nitric
oxide synthase.
Turmeric-derived curcumin is also one of the natural blood thinners as it is known to have powerful anti-coagulant
properties. This is due to its ability to inhibit
platelet aggregation and the formation of fibrinogen.
5. Vitamin C and Cytokine Storm
Vitamin C may be one of the most well-known immune nutrients that protect against immune deficiencies and which supports the prevention and recovery from the common cold and upper-respiratory issues, and also protects your cardiovascular system, eyes, skin, and other parts of your body. Research has found that vitamin C may help to optimize the innate and adaptive immune system.
Vitamin C might help prevent COVID-19 and also lessen
the inflammatory reactions behind some severe COVID-19
cases, according to a review of research on the topic published in the latest issue of the journal
Nutrition.
Do take note that the vitamin C dosages given in the
hospitals intravenously are different from those over
the counter vitamin C supplements. Therefore, when you
come across studies on vitamin C, you need to
differentiate those that are given intravenously vs oral
vitamin C.
Vitamin C and COVID-19
Check out the evidence tracker on vitamin C and COVID-19
from c19vitaminc.com (constantly updated).
Safety: The U.S. Recommended Dietary
Allowance (RDA) for vitamin C is 75 to 120 milligrams
per day. Taking large doses of vitamin C (ascorbic
acid) on a regular basis lowers your level of copper,
so if you are already deficient in copper and take
high doses of vitamin C, you can compromise your
immune system.
While generally considered safe even in high doses,
way too much vitamin C — anything above 2,000
milligrams daily—can cause headaches, insomnia,
diarrhea, heartburn, and other issues.
Temporarily taking megadoses of vitamin C supplements to combat a case of the cold or flu is likely not going to cause a problem.
Vitamin C, Omicron and Deltacron
Will Vitamin C Work Against Omicron or Deltracron?
Vitamin C is not variant specific because it's primary
mode of action is to support the body’s immune system
which reacts in a variety of ways against viral
attack, not just in a specific antibody reaction to a
specific spike protein.
Related: Best Vitamin C Supplement
6. Nigella Sativa (Black Seed Oil) and Cytokine Storm
Nigella sativa (N. sativa) is a small flowering plant that
grows in Southwest Asia, the Middle East, and Southern Europe
(Source). This shrub produces fruit with tiny black seeds. Commonly
referred to as black seed, N. sativa seeds go by many other
names, such as black cumin, black caraway, nigella, fennel
flower, and Roman coriander (Source).
Black seed oil is extracted from N. sativa seeds and has been used in traditional medicine for over 2,000 years due to its many therapeutic benefits.
7. Melatonin and COVID-19
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland
in the brain, mainly during the night, that helps
regulate circadian rhythms [Source]. Its levels decrease with aging.
Most melatonin supplementation studies have evaluated its ability to control
sleep and wake cycles, promote sleep, and reduce jet
lag.
The potential utility of melatonin in treating
COVID patients has not gone unnoticed, with a PubMed
search combining melatonin and COVID producing more
than 50 citations.
Check out the evidence tracker on melatonin and COVID-19 from c19melatonin.com (constantly updated).
Check out the evidence tracker on melatonin and COVID-19 from c19melatonin.com (constantly updated).
As of October 2022, there are more than 15
published clinical studies of melatonin for treatment and prevention in
COVID-19 and the results are promising even when it's
given as a late treatment.
Melatonin and COVID-19
Production of melatonin diminishes with age,
contributing to immune dysfunction and increasing
oxidative stress, inflammation, and infection
susceptibility (Ref). In addition, infectious viruses can suppress
melatonin production, disrupting circadian controls
and impairing immune function (Ref).
A study published in the Nature (Sefik 2022) by researchers from Yale University (USA) has found
that the SARS-CoV-2 virus directly infects certain
immune cells that leads to inflammasome activation
that ultimately contributes to the hyperinflammatory
state of the lungs.
According to a study published in Antioxidants (Arioz 2021), melatonin is able to inhibit inflammasome
activation.
According to a review (Cardinali et al. 2020), melatonin might also counteract the consequences of
COVID-19 via salutary effects on the sleep/wake
cycle and more generally on chronobiology, as well
as through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory
effects.
Based on melatonin’s therapeutic potential and
well-established safety profile, it has been suggested
those at higher risk for severe illness and
complications from viral respiratory infection,
including the elderly and those with chronic medical
conditions, may benefit most from regular use of 3–10
mg melatonin at bedtime (Ref).
Fluvoxamine (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor) might also
exert beneficial effects in COVID patients through its
well-characterized ability to substantially increase
(~ 2–3-fold) night-time plasma levels of melatonin.
This increase appears to result from fluvoxamine’s
inhibition of the melatonin-metabolizing liver
enzymes (von Bahr et al. 2000).
An Iranian randomised controlled trial (Arch Med Res 2021), studied 74 mild to moderate
hospitalized patients. The study showed that adjuvant
use of melatonin has a potential to improve clinical
symptoms of COVID-19 patients and contribute to a faster
return of patients to baseline health.
Some researchers have suggested high doses of melatonin,
ranging from 50 to 200 mg twice daily, might help treat
patients hospitalized for severe acute respiratory
illness (Ref).
In a small Philippine case series study of 10 hospitalised COVID-19 patients,
high dose melatonin (hdM) was given in addition
(adjuvant) to standard therapy. According to the
authors:
"High dose melatonin may have a beneficial role in
patients treated for COVID19 pneumonia, in terms of
shorter time to clinical improvement, less need for
MV, shorter hospital stay, and possibly lower
mortality."
Safety: If you take a melatonin supplement,
be careful: Too much can cause daytime sleepiness. There is no federal RDA nor any formal advice on
supplement dose ranges. Based on an on-going Spanish study, a 2 mg daily dose protocol is being investigated for
prevention of COVID-19. Do take note that the dosage for
'prevention' and 'treatment' is different, For
prevention or maintenance, a lower dosage is normally
recommended whereas a 'treatment' or 'therapeutic'
dosage is normally higher.
Typical doses of 1–10 mg/day melatonin appear to be safe
for short-term use (Source). Reported side effects, which are usually minor,
include dizziness, headache, nausea, upset stomach,
rash, and sleepiness. However, some reports have linked
high blood levels of melatonin with delayed puberty and
hypogonadism.
Studies have not evaluated melatonin supplementation during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but some research suggests that these supplements might inhibit ovarian function (Source). Therefore, some experts recommend that women who are pregnant or breastfeeding avoid taking melatonin.
Studies have not evaluated melatonin supplementation during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but some research suggests that these supplements might inhibit ovarian function (Source). Therefore, some experts recommend that women who are pregnant or breastfeeding avoid taking melatonin.
- Nature's Bounty Melatonin 5 mg > One tablet
before bedtime (Amazon)
8. Glutathione, NAC and COVID-19
Does NAC prevent cytokine storm in COVID? According to
this paper (2021), SARS-CoV2 infection impairs the metabolism
and redox function of cellular glutathione. According to
the authors, NAC can prevent this damage and the role of
NAC in COVID-19 therapy is worth investigating.
NAC inhibits cellular entry and replication of some
respiratory viruses, assists in clearing thickened
mucous from the airways, suppresses inflammatory
signaling, and may help mitigate viral infection-induced
cytokine storm (Ref).
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is a precursor to glutathione. It is an antioxidant
and increases glutathione levels in the body (Source). NAC has mucolytic activity, so it helps reduce
respiratory mucus levels. Laboratory research suggests
that NAC might boost immune system function and suppress
viral replication. NAC also decreases levels of
interleukin-6 and has other anti-inflammatory effects.
Much of the research on NAC has used an inhaled, liquid form of this compound. This form—which is classified as a drug, not a dietary supplement—is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a mucolytic agent and for decreasing respiratory secretion viscosity (Source). Products containing NAC are also sold as dietary supplements.
NAC and COVID-19
For a compilation of more than 10 studies of NAC and
COVID-19, check out the list of studies here (constantly updated).
However, in terms of early treatment, the improvement
rate is not as impressive as the other alternatives
i.e. quercetin, black seed oil and vitamin A.
Studies published in ACS Infectious Disease (ACS Infect Dis. 2020) and Antioxidants proposed that glutathione plays a crucial role
in the body's fight against the severe inflammatory
response triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The
research group in the ACS Infectious Disease study
called it the “most likely cause of serious
manifestations and deaths in COVID-19 patients.”
Foods that have a positive impact on glutathione
production include cruciferous vegetables such as
broccoli, green tea, curcumin, rosemary and milk
thistle. Getting quality sleep may also help.
Different types of exercise can influence your levels as well. In one study, researchers enrolled 80 healthy but sedentary volunteers to measure the type of exercise that may have the greatest effect. They found that aerobic training in combination with circuit weight training showed the greatest benefit.
Different types of exercise can influence your levels as well. In one study, researchers enrolled 80 healthy but sedentary volunteers to measure the type of exercise that may have the greatest effect. They found that aerobic training in combination with circuit weight training showed the greatest benefit.
Consider taking around 500 milligrams/day of NAC,
as it helps prevent blood clots and is a precursor
for your body to produce the important antioxidant
glutathione.
Why are some retailers and Amazon no longer
selling NAC? The US FDA made it clear in 2020
that it considers NAC to be a drug and not a
dietary supplement, so, for legal reasons, some
companies have stopped selling it in United
States.
What Is the Primary Cause of Severe COVID-19
Illness: Glutathione or Vitamin D Deficiency?
The hypothesis that vitamin D (VD) deficiency is
responsible for severe manifestations and death in
COVID-19 patients has been proposed and is actively
being discussed by the scientific community.
Several studies reported that glutathione levels
positively correlate with active vitamin D. (PubMed, PubMed)
Interestingly, a recent experimental study (PubMed) showed that Glutathione deficiency and the
associated increased oxidative stress epigenetically
alters vitamin D regulatory genes and, as a result,
the suppressed gene expression decreases Vitamin D
production, ultimately leading to a secondary
deficiency of vitamin D. This study provides important
information that glutathione is essential for the
control of endogenous vitamin D production and
demonstrates potential benefits of Glutathione
treatment in reducing the deficiency of vitamin D.
Taken together, these findings suggest that
glutathione deficiency rather than vitamin D
deficiency is a primary cause underlying biochemical
abnormalities, including the decreased biosynthesis of
vitamin D, and is responsible for serious
manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients.
NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine) vs Glutathione
N-acetyl L-cysteine (NAC), as a precursor of
glutathione, helps to replenish intracellular
glutathione, a vital cellular antioxidant. NAC has a low
molecular weight and is well absorbed via oral
administration as compared to glutathione.
NAC may also protect against coagulation problems
associated with COVID-19, as it counteracts
hypercoagulation and breaks down blood clots.
Glutathione and Zinc
To improve your glutathione, you need zinc, and zinc in
combination with hydroxychloroquine (a zinc ionophore or
zinc transporter) has been shown effective in the
treatment of COVID-19.
Glutathione and Molecular Hydrogen
One of the best ways to increase glutathione, though, is
molecular hydrogen. Molecular hydrogen does so
selectively and will not increase glutathione
unnecessarily if you don’t need it. You can view Tyler
LeBaron’s lecture on the details of how it does this in
“How Molecular Hydrogen Can Help Your Immune System.”
Glutathione and Selenium
Selenium is also important, as some of the enzymes
involved in glutathione production are
selenium-dependent.
Glutathione and Blood Clot
Glutathione is also one of the natural blood thinners as it is known to reverse the build-up of
plaque and lessen the tendency of abnormal blood
clots.
For NAC contra-indications, check out here.
9. Green Tea (EGCG)
Quercetin and EGCG act as zinc ionophores (J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014), the same mechanism of action that
hydroxychloroquine has via helping zinc pass the
cell wall where it might halt viral replication.
However, an underpowered observational study from Japan suggests that only a large consumption
of green tea might be preventative against Covid, pointing
to the bioavailability issue. Unfortunately, high green tea consumption is not recommended for your
kidneys.
10. Fish Oil (Omega-3 Fatty Acids) and Omega-6
That are more than a dozen studies on-going that
examine the effect of EPA and/or DHA on the prevention
of or lessening of symptoms of COVID-19. Check out the
evidence tracker on Omega 3 and COVID-19 from c19early.com (constantly updated).
Omega-3 Fatty Acids are part of the I-Recover treatment protocol for Long Haul or Post-COVID syndrome, launched
on June 16, 2021 by the FLCCC (Front Line COVID-19
Critical Care Alliance).
A pilot study (Jan 2021) suggests that patients with the most
omega-3s in their system were 75% less likely to die
from COVID-19. The pilot study was conducted using
blood drawn from 100 patients treated for COVID-19 at
the Cedars Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. The
postulated mechanism of action is the well known anti
inflammatory role of higher omega-3 levels, which may
helped quell the so-called 'cytokine storm' observed
in some severe and/or fatal COVID-19 cases.
This protection may have come from the effect EPA and DHA have on the body. An opinion paper published in June 2020 in the journal Frontiers in Physiology expounded on how "EPA and DHA supplementation can alter many biological pathways which may have a direct influence in the outcome of COVID-19."(Front. Physiol., 19 June 2020) The writers listed the many nutrients that play a key role in managing a cytokine storm and continued:
"Among these micronutrients, LC-PUFAs (long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids) such as EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are noteworthy because of their direct influence in the immunological response to viral infections.
Among these complex immunomodulatory effects, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1ß (IL-1β)—because of the suspected central regulatory role in the "cytokine storm"—should be highlighted."
Accumulating evidence shows omega-3 fatty acids, administered orally or intravenously, may help control inflammation and improve outcomes in critically ill patients, including those with ARDS.489 A meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials with a total of 1,280 critically ill patients with ARDS found supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids, in combination with gamma-linolenic acid (a less-inflammatory omega-6 fatty acid) and antioxidants, improved markers of lung function; however, only hourly administration, rather than large bolus intravenous dosing, was associated with reduced mortality. Although reductions in mechanical ventilation and length of stay in intensive care were seen, these effects did not reach statistical significance (Ref).
An observational study in 100 patients hospitalized with a severe acute viral respiratory illness found higher levels of EPA plus DHA were associated with lower mortality, though the effect was not statistically significant, possibly due to the small number of participants (Ref). During an outbreak of a severe viral respiratory infection, another study found countries with the highest intake of omega-3 fatty acids from marine sources had lower mortality rates than other regions of the world (Ref). The same research group used computer modeling to show how omega-3 fatty acids might bind to the highly infectious virus and interfere with its ability to enter cells (Ref).
Evidence suggests the omega-3 fats EPA and DHA
affect biological pathways that may have direct
influence in the outcome of COVID-19.
EPA and DHA have a direct influence in the immunological response to viral infections and can modulate immune response and function.
Animal-based omega-3 fats, especially DHA, also help prevent thrombosis (a blood clot within a blood vessel) by decreasing platelet aggregation. Hypercoagulation is another complication of severe COVID-19 infection that can have lethal consequences.
Omega-3 also lowers your risk of lung dysfunction, protects against lung damage and secondary bacterial infections, and improves mitochondrial function.
Research shows that by lowering triglycerides, the risk of developing a cytokine storm is diminished. Omega-3 supplementation is known to lower triglycerides, but krill oil does so more effectively than fish oil.
The British Rhinological Society's Guidelines for the
Management of New Onset Loss of Sense of Smell During
the COVID-19 Pandemic advises that that fish oil
supplementation (2,000 mg of omega-3 fatty acids/day)
may be beneficial when used in addition to standard
treatment (olfactory training, oral steroids and steroid
rinses) (Hopkins, Clin Otolaryngol 2020). This position is not based on a clinical trial of
fish oil in COVID-19 patients but on limited animal and
human research suggesting that omega-3 fatty acids may
be beneficial for loss of smell due to olfactory nerve
damage.
Related: Best Fish Oil Supplements
11. B Vitamins and COVID-19
Thiamine (vitamin B1), a water-soluble B-complex vitamin,
is rapidly depleted during times of metabolic stress,
including severe illness. Thiamine deficiency is common in
hospitalized patients, especially those with critical
illness (Ref). Thiamine is needed for cellular energy production and
helps regulate reduction-oxidation balance, immune
function, nervous system function, and vascular function
(Ref).
Thiamine, at 200 mg twice daily, reduced mortality in
patients with septic shock and thiamine deficiency, and
laboratory research suggests it may inhibit the
hyper-inflammatory immune response that accompanies cytokine
storm (Ref). It is a key therapeutic in the MATH+ protocol
(methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid [vitamin C], thiamine,
and heparin, plus other supportive nutrients and
medications), a treatment strategy proposed for managing
advanced stages of severe acute viral respiratory illness
(Ref). Although high-quality clinical evidence is lacking, two
US hospitals implementing the MATH+ protocol in patients
with a severe acute viral respiratory illness reported
mortality rates that were approximately one-quarter of those
reported from other US hospitals using standard care (Ref).
In a study in Saudi Arabia (Al Sulaiman et al. Crit Care 2021), 738 critically ill COVID-19 patients from two centers
were included in the study. The in-hospital death rate and
30-day death rate were significantly lower in the group that
received thiamine as an adjunctive treatment (a therapy
given in addition to standard therapy). In addition, the
thiamine group also were less likely to have blood clot
during ICU stay.
Another study of COVID-19 patients with severe symptoms
found 26.3% among diabetics with COVID-19 were vitamin B1 deficient.
Adequate amounts of folate, vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 are
also needed for your body to make the amino acid cysteine.
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is a supplement form of cysteine.
Consuming adequate cysteine and NAC is important for a
variety of health reasons — including replenishing the
most powerful antioxidant in your body,
glutathione.
A study published in November 2020 from Singapore (CW Tan, Nutrition 2020), found that those who were started on a daily oral
dose of vitamin D3 (1,000 IU), magnesium (150 mg) and
vitamin B12 (500 mcg) within the first day of
hospitalisation and continued up to 14 days were
significantly less likely to require oxygen therapy and
further intensive care.
A case series (published in September 2020) of 9 elderly
COVID-19 patients treated with a combination of NMN,
zinc, betaine and sodium chloride resulted in rapid
improvement.
The topic 'B vitamins' is a complicated subject and
that's probably why they are called 'B Complex'.
B vitamins may constitute a long list, but each one is
important for different reasons. B vitamins are
especially effective in boosting your immunity when you
combine the foods containing them so they can all work
together for maximum effect. These include vitamin B1
(thiamin), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic
acid) and B7 (biotin).
B12, also known as cobalamin, is a powerful cold- and flu-fighting nutrient in your system, as is vitamin B6, another important, germ-combating vitamin that naturally benefits and strengthens your immune system and even protects against the damaging effects of air pollution.
Vitamin B9 and folic acid help repair tissues and aid in cell metabolism and immune support. They’re found in dark leafy greens, wild-caught, cold water fish like herring, mackerel, sardines, anchovies and wild-caught Alaskan salmon, and pastured, organic chicken.
B12, also known as cobalamin, is a powerful cold- and flu-fighting nutrient in your system, as is vitamin B6, another important, germ-combating vitamin that naturally benefits and strengthens your immune system and even protects against the damaging effects of air pollution.
Vitamin B9 and folic acid help repair tissues and aid in cell metabolism and immune support. They’re found in dark leafy greens, wild-caught, cold water fish like herring, mackerel, sardines, anchovies and wild-caught Alaskan salmon, and pastured, organic chicken.
Niacin or vitamin B3 is a precursor to nicotinamide
adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). There are three main forms of niacin, which are dietary precursors to nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide (NAD). These are nicotinamide riboside,
nicotinic acid and nicotinamide.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential
cofactor in all living cells that is involved in
fundamental biological processes. NMN (Nicotinamide
MonoNucleotide), is also another precursor to NAD.
Related: Niacin and COVID-19 - Is Niacin a Missing Piece of the COVID
Puzzle?
12. Probiotics
Probiotics are living non-pathogenic microorganisms that,
when administered in adequate amounts, can have a
positive impact on health. Bacteria in the
Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium genera, as well as
Streptococcus thermophiles and Saccharomyces
boulardii, are examples of common probiotics (Ref).
- High gut diversity of bacteria type
- Abundance of bifidobacteria (p<0.0001 which means the effect was “highly statistically significant” and unlikely to have happened “by chance”)
Physiological changes in the human microbiota with age
leads to a “physiological dysbiosis”, with less
diversification in microbial composition, aggravated in
case of comorbidity (hypertension, diabetes, chronic
inflammatory bowel diseases, etc.) (Ref). Therefore, to establish the condition of eubiosis
(healthy condition), “good” bacteria are required. The
concept of probiotics as a food with positive effects was
firstly used by Parker RB in 1974 and then recognized by
the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), and more
recently by the Word Health Organization (WHO) (Ref).
The first quadrupled blinded randomised controlled trial (Gutiérrez-Castrellón et al., Gut Microbes) on a novel probiotic formulation demonstrated that complete
remission on day 30 was boosted from 28% to 53%.
13. Molecular Hydrogen
Molecular hydrogen has been tested in several registered clinical trials right now as a potential treatment option for COVID-19.
There have been a plethora of studies on hydrogen’s effects
on inflammation, in particular in regulating/controlling
inflammatory cytokines. For example:
Beyond the existing scientific studies that show a reason for excitement, hydrogen gas is also now being recommended in China as a therapy for individuals suffering from COVID-19, and there are very positive recorded anecdotal reports from patients.
The science behind the virus and potential treatment is, of
course, far more complex than this, and we do not intend to
simplify the situation whatsoever. Nonetheless, the
potential here is interesting — especially when you factor
in the safety factor of molecular hydrogen. We will have to
see what happens as the science develops and the clinical
trials are conducted, and we will update this article with
more information as it becomes available.
- A group of scientists in China suggested that hydrogen-rich solution therapy may be a safe, reliable, and effective treatment for Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS) induced by influenza and other viral infectious diseases (SOJ Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017).
- In a 2017 lab study published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology, “HRW (hydrogen rich water) treatment significantly reduced EtOH-induced increases in serum alanine amino transferase, aspartate aminotransferase, triglycerol and total cholesterol levels, hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin (IL)-6.”
- Another study in 2013 stated “The serum levels of cytokines such as IL-10, TNF-α, IL-12p70, and GM-CSF of mice administered with HW (hydrogen water) was significantly reduced as compared to PW (placebo water) group.”
Beyond the existing scientific studies that show a reason for excitement, hydrogen gas is also now being recommended in China as a therapy for individuals suffering from COVID-19, and there are very positive recorded anecdotal reports from patients.
- The epidemiologist who discovered the SARS Coronavirus back in 2003, Dr. Zhong Nanshan, is now recommending H2 therapy for COVID-19 — you can watch the video where he does so here.
- Other individuals in the scientific community are talking about hydrogen as a possible treatment for COVID-19.
The first preliminary report on COVID-19 patients (n=90)
from China has been published demonstrating that
Hydrogen/Oxygen mixed gas inhalation has superior effects
compared to Oxygen alone (Journal of Thoracic Disease. 2020).
14. Vitamin A and COVID-19
Summary results of 10 vitamin A and COVID-19 studies
are available on this dedicated webpage: c19early.com/va.
Scientists are also investigating if taking vitamin
A could aid patients who have lost their sense of
smell due to COVID-19. The 12-week 'Apollo study' would use nasal drops containing the vitamin to
treat individuals who have lost or changed their
sense of smell.
15. Lactoferrin
Summary results of 4 Lactoferrin and COVID-19
studies are available on this dedicated
webpage: https://c19early.com/lf .
Lactoferrin may slow pathogen multiplication through its iron binding capacity. While iron is required for DNA replication and energy production, the presence of excess iron increases free radical generation, stimulates inflammatory processes, and exacerbates viral infection by promoting increased viral replication (Ref). Furthermore, patients with a severe acute viral respiratory infection have been found to have elevated levels of ferritin, and these levels correlated with increased risk of death (Ref). In its iron-free state (apolactoferrin), lactoferrin can sequester pro-oxidant free iron, lowering oxidative stress and suppressing the growth of pathogens, and possibly mitigating the serious complications of infection (Ref).
In a pilot trial, 75 patients who tested positive for an acute viral respiratory tract infection were treated at home with a liposomal preparation of a combination of 32 mg bovine lactoferrin with 12 mg vitamin C, with or without 10 mg liposomal zinc, four to six times daily for 10 days. In addition, lactoferrin nasal drops, mouth spray, and aerosol were used as needed by participants with headaches, loss of sense of smell and taste, nasal congestion, dry cough, or difficulty breathing. After 48 hours, all symptoms had diminished except loss of smell and taste, and by day five, all infected participants recovered from their illness with only loss of smell and taste remaining as residual symptoms (Ref).
16. Selenium
Selenium plays a role in immune cell function and activation through its incorporation into enzymes and other proteins. It also reduces infectivity, replication, and virulence of several respiratory viruses (Ref). Sodium selenite, a form often used in supplements, has been found to block an infectious respiratory virus from entering cells by interacting with its spike protein in the laboratory (Ref).
Selenium works closely with vitamin E and cysteine to
regulate oxidation and reduction balance and
neutralize free radicals, and can help reduce
inflammatory signaling by controlling oxidative stress
(Ref). Poor selenium status may also increase the
likelihood of induction of excess inflammation due to
cytokine storm (Ref).
The soil concentration of selenium varies geographically around the world, affecting selenium status and resulting in endemic insufficiency and deficiency (Ref). A study comparing COVID-19 survival to regional selenium status during a major outbreak in China found survival was more likely in high-selenium regions (Ref). A study done during an outbreak in Germany found higher selenium and selenium-containing protein levels in COVID-19 infection survivors versus non-survivors (Ref).
Blood selenium levels have been noted to diminish in patients with critical illness, and lower levels are correlated with more severe illness and lower chance of survival (Ref). A meta-analysis of 19 randomized controlled trials found intravenous selenium supplementation in critically ill patients reduced total mortality (but not 28-day mortality) and shortened the length of hospital (but not intensive care unit) stay (Ref).
In a randomized controlled trial in 40 patients with
ARDS, those who received sodium selenite intravenously
for 10 days had increased glutathione levels,
decreased inflammatory cytokine levels, and improved
lung function compared with those who received saline
(placebo). However, there were no differences in
survival or intensive care unit stay (Ref).
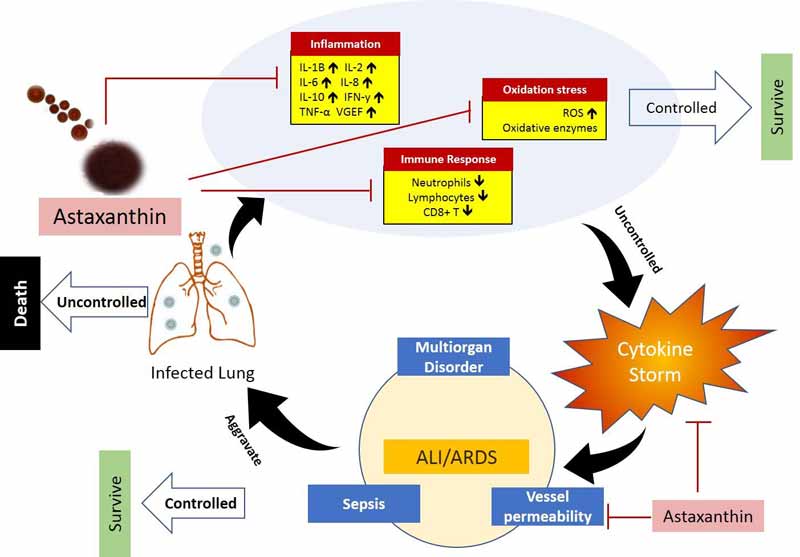
17. Astaxanthin
The paper (SSRN) “COVID-19: Potential of Microalgae Derived Natural Astaxanthin as Adjunctive Supplement in Alleviating Cytokine Storm,” published April 21, 2020, on the research library website SSRN, addresses the use of astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant supplement derived from microalgae. The full paper is downloadable from the link.As explained in this paper, astaxanthin has a very unique molecular structure that allows it to penetrate the bilayer membrane of cells. The ability to quench reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals in both the inner and outer layers of the cellular membrane allows it to provide superior protection against oxidative stress, compared to other antioxidants.
Vitamin E and beta-carotene, for example, only work in the inner side of the membrane, and vitamin C only works on the outer side.

In short, astaxanthin ticks many important boxes when it comes to ameliorating COVID-19, including immune response regulation and the enhancement of both cell-mediated and humoral immune responses, as well as the simultaneous protection against oxidative damage and inflammation.
18. Resveratrol
Dormant cytomegalovirus (CMV) is carried by 70-90% of the adult population and is
reactivated by inflammation. One third of patients in hospital intensive care
units reactivate CMV which doubles their mortality
rate. There is agreement that Covid-19 co-infection with cytomegalovirus is
associated with higher rates of mortality in older
people who have an aged (senescent) immune system.
Cytomegalovirus also dulls the vitamin D
receptors thus preventing the active form of vitamin D
to enter living cells.
Resveratrol binds to and activates the vitamin D
receptors, thus allowing cells in the body to respond to
vitamin D.
The daily value (DV) of resveratrol has not been
established. Recommended dosages from manufacturers
vary from 150 mg to 300 mg daily.
Resveratrol also inhibits blood clots associated
with Covid-19 infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Elderberry and Cytokine Storm
Conclusion
Macronutrients and micronutrients are essential nutrients to a human body. Low levels of essential nutrients cause the immune system to be operating at a sub-optimal level.
Optimizing your immune system is critical to improve your health whether
there is a pandemic or not.
Cytokines are an important part of your immune response. However, when your body releases excessive or uncontrolled levels of cytokines it results in hyper-inflammation called a cytokine storm. A cytokine storm may lead to serious complications and even death in serious COVID-19 cases and in other infections.
Optimizing your immune system with diet and lifestyle changes are critical to improving your health and to decrease your risk of a cytokine storm. However, therapeutics, vaccines and other physical strategies such as social distancing and mask wearing are also needed in order to protect yourself and your loved ones. It doesn't have to be an 'either or' situation. Combination strategies are normally more effective.
Cytokines are an important part of your immune response. However, when your body releases excessive or uncontrolled levels of cytokines it results in hyper-inflammation called a cytokine storm. A cytokine storm may lead to serious complications and even death in serious COVID-19 cases and in other infections.
Optimizing your immune system with diet and lifestyle changes are critical to improving your health and to decrease your risk of a cytokine storm. However, therapeutics, vaccines and other physical strategies such as social distancing and mask wearing are also needed in order to protect yourself and your loved ones. It doesn't have to be an 'either or' situation. Combination strategies are normally more effective.
Related:
Quercetin vs Astaxanthin
This article is subject to change as new evidence emerge. One Day MD
has not performed independent verification of the data contained in
the referenced materials, and expressly disclaims responsibility for
any error in the literature.
Note: To get 5% OFF, please use this coupon code: DRFRANCIS
Disclaimer: The information on this website is not intended to
replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care
professional and is not intended as medical advice. It is intended
as a sharing of knowledge and information from the research and
experience of third party sites. If you are pregnant, nursing,
taking medication, or have a medical condition, consult your health
care professional before using products based on this content.
Z-Stack Supplement
In an effort to make it easier for patients, Dr Vladimir Zelenko has developed an oral supplement that contains all four key ingredients: vitamin C, quercetin, vitamin D3 and zinc. It’s referred to as 'Z-Stack Supplement'.
Z-Stack Vitamin cocktail provides key ingredients needed in order to help your body fight off this deadly invader. The Z-Stack Vitamins are Kosher certified, GMP certified and made in the USA.
The cost of the Z-STACK vitamin cocktail is $55 per bottle for a one month supply.
Where to buy Z-Stack: Z-stack is available on Dr Zelenko's website. Here is the link: Z Stack Supplement
Note: To get 5% OFF, please use this coupon code: DRFRANCIS

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)



.png)



.png)
.png)






Comments
Post a Comment