15 Best Drug Combination Treatment Studies for COVID-19 (2022)
Information related to the COVID-19 pandemic has been overwhelming and confusing as well. Information is all over the place and various groups are giving conflicting statements. How do you make sense from all these fragmented information?
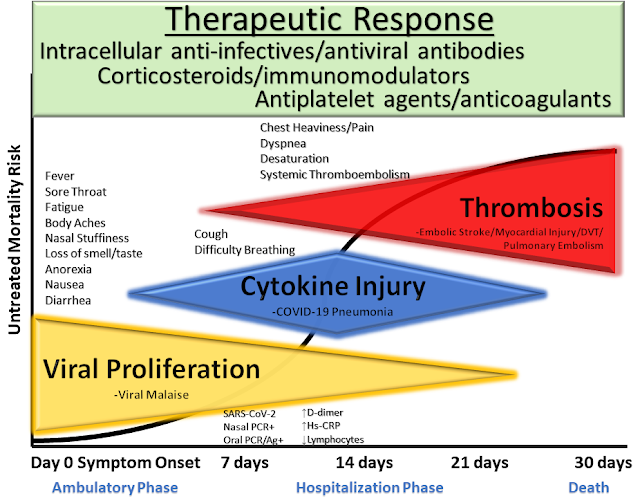 |
| McCullough et al. Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2020 |
As of December 2021, there are more than 1,000 studies that have been published on treatments for COVID-19. You can review the details of these trials on c19early.com. New ones are being added every day. The aim of this article is to organise and summarise the best available evidence in one place.
Most doctors know the need to focus now on early treatment as the most
immediate and practical way to reduce hospitalizations and death. This is your
guide to help you know your options, and to use with your personal physician.
Most reviews analyze the drug from a mono-therapy perspective and tend to draw
conclusion on whether that one drug is effective or not for COVID-19. However
in reality, we do know that most doctors don't use only one drug for
treatment. Treatments for COVID-19 are given as a multi-drug protocol or
combination therapy. Most treatments are typically used in combination, which
may be
significantly more effective.
In addition, most comparative studies are comparing a new treatment group with
a 'standard of care' group as the control group. However, the 'standard of
care' group may vary from hospital to hospital and country to country as well.
You will normally need to dive into the full paper to review what other
treatments are given as the 'standard of care'.
In a retrospective cohort study published in the Lancet, it is found that 50% of COVID-19 patients who died had bacterial
co-infections in pneumonia. Bacterial coinfections have also been shown to
increase the risk of mortality for COVID-19 patients [Chen et al].
Below, we look at the best available evidence for proven combination treatment for COVID-19 and summaries of the evidence for each combination.
Best Early Combination Treatment Studies for COVID-19
1. Borody et al.,
TrialSite News (Preprint)
- Oct 2021
Combination Therapy For COVID-19 Based on Ivermectin in an Australian
Population (n=600)
Retrospective 600 PCR+ outpatients in Australia treated with ivermectin, zinc,
and doxycycline, showing significantly lower mortality and hospitalization
with treatment. This trial uses a synthetic control group, and the preliminary
report provides minimal details.Death, 92.3% lower, RR 0.08, p = 0.03, treatment 0 of 600 (0.0%), control 6 of 600 (1.0%).
Hospitalization, 92.9% lower, RR 0.07, p < 0.001, treatment 5 of 600 (0.8%), control 70 of 600 (11.7%).
Dosage 24mg days 1-10, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with zinc and doxycycline) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Related: Topelia Australia launches US$25M Series A call for COVID-19 ATT Ziverdox
2. Okogbenin et al., Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal
doi:10.4103/npmj.npmj_532_21 (Peer Reviewed) - Sep 2021
Retrospective 300 COVID-19 patients in Nigeria treated with ivermectin,
zinc, vitamin C, and azithromycin, reporting no deaths.
- Ivermectin was given at a dose of 200 μg/kg, day 1, then 100 μg/kg/day, from day 2 to day 5.
- Azithromycin was given at a dose of 500 mg daily for 10 days,
- Zinc sulfate at a dose of 40 mg daily and
- Vitamin C at a dose of 500 mg daily for 10 days.
In addition, some received oral Augmentin (Co-Amoxiclav) 87 (29.0%),
sedatives 69 (23.0%), steroids 57 (19.0%), oxygen therapy 16 (5.3%),
intravenous antibiotics 10 (3.3%) and anticoagulant (Enoxaparin) 11
(3.7%). Oral Augmentin was given at a dose of 1 g b.d, subcutaneous
Enoxaparin at a dose of 40–80 mg daily and oral dexamethasone, 8 mg
Stat, then 4 mg b.d for 5–7 days.
Among all patients treated only 5 (1.7%) and 3 (1.0%) developed
pneumonia and sepsis, respectively. As at October 26, 2020, majority 287
(95.7%) of the patients had been discharged with only one (0.3%)
referral; 12 (4.0%) patients had home-based care with monitoring through
telephone. There was no death recorded.
Authors conclude that early treatment is critical.
3. Marik et al. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2020:1–7. (Aug 2020)
- Methylprednisolone 80 mg loading dose, followed by 40 mg q 12 hourly for at least 7 days and until transferred out of ICU. In patients with an increasing C-reactive protein (CRP) or worsening clinical status increase the dose to 80 mg q 12 hourly (and then 120 mg if required), then titrate down as appropriate.
- Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) 3 g IV q 6 hourly for at least 7 days or until transferred out of ICU. Note caution with point-of-care (POC) glucose testing (see below).
- Thiamine 200 mg IV q 12 hourly for at least 7 days or until transferred out of ICU.
- Heparin: Unless contraindicated we suggest FULL anticoagulation (on admission to the ICU) with enoxaparin, i.e. 1 mg kg s/c q 12 hourly (dose adjust with CrCl < 30 ml/min). Unfractionated heparin is suggested with CrCl < 15 ml/min. Monitor anti-Xa activity in at risk patients (see below)
- Supplemental oxygen with high flow nasal canula with proning (cooperative repositioning) and epoprostenol as required. Intubation should be avoided if at all possible.
The Frontline COVID-19 Critical Care Expert Group (FLCCC), a group of emergency medicine experts, have reported that, with the combined use of 6 g/day intravenous vitamin C (1.5 g every
6 h), plus steroids and anticoagulants, mortality was 5% in two ICUs
in the US (United Memorial Hospital in Houston, Texas, and Norfolk
General Hospital in Norfolk, Virginia), the lowest mortality rates in
their respective counties .
Update (Dec 2021): The latest MATH+ protocol has been updated to include multiple first line adjunctive
therapies:
Ivermectin
- Hospitalized patients
- 0.6 mg/kg per dose — daily 2 (take with or after a meal)
- For 5 days or until recovered
Nitazoxanide
- Hospitalized patients
- 500mg twice daily — (take with or after a meal)
- For 5 days or until recovered
Dual Anti-Androgen Therapy
- Hospitalized patients
- 1. Spironolactone 100mg twice daily
- 2. Dutasteride 2mg on day 1, followed by 1mg daily — or Finasteride 10mg daily
- 14 days or until discharge from hospital
- ICU Patients
- 1. Flutamide 250mg TID — or Bicalutamide 150mg daily
- 2. Dutasteride 2mg on day 1, followed by 1mg daily — or Finasteride 10mg daily
- 14 days or until discharge from hospital
Vitamin D
- Hospitalized patients
- Calcitriol: 0.5mcg on day 1, then 0.25mcg daily
- 7 days
Melatonin
- Hospitalized patients
- 6–12mg PO at night
- Until discharge
4. Ried et al., Cureus, Therapies to Prevent Progression of COVID-19, Including Hydroxychloroquine, Azithromycin, Zinc, and Vitamin D3 With or Without Intravenous Vitamin C: An International, Multicenter, Randomized Trial
doi:10.7759/cureus.19902
(Peer Reviewed) - Nov 2021
All but one patient (99.6%; n = 236/237) treated with HCQ, AZM,
and zinc with or without high-dose IV vitamin C (IVC) fully
recovered. Additional IVC therapy contributed significantly to a
quicker recovery (15 days versus 45 days until discharge; p =
0.0069).
The placebo group received placebo in addition to standard of care. (n=200)
The median recovery time was 9 days
Hydroxychloroquine, Azithromycin, Zinc, and Vitamin D3 With
Intravenous Vitamin C (n=75)
- Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was given as 400 mg per oral (PO) once a day for one day, followed by 200 mg once a day for six days.
- Azithromycin (AZM) was given as 500 mg PO on day 1, followed by 250 mg PO once daily for four days.
- Zinc citrate was given as 30 mg elemental zinc PO daily for 14 days.
- Vitamin D3 was given as 5,000 IU PO daily for 14 days.
- IV vitamin C (sodium ascorbate) was given as 50 mg/kg every six hours on day 1, followed by 100 mg/kg every six hours (four times daily, 400 mg/kg/day) for seven days
Hydroxychloroquine, Azithromycin, Zinc, and Vitamin D3 Without
Intravenous Vitamin C (n=162)
5. Chowdhury (RCT) - A Comparative Study on Ivermectin-Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin Therapy on in mild to moderate COVID-19 Patients - Jul 2021
Ivermectin-Doxycycline (n = 60)
Ivermectin 200µgm/kg single dose + Doxycycline 100mg BID for
ten days in group A
All subjects in Group A reached a negative PCR, at a mean
of 8.93 days, and reached symptomatic recovery, at
a mean of 5.93 days, with 55.10% symptom-free by the fifth
day.
Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin (n = 56)
Hydroxychloroquine 400mg for the first day, then 200mg BID for
nine days + Azithromycin 500mg daily for five days in group B
In group B, 96.36% reached a negative PCR at a mean of 9.33 days and were symptoms-free at 6.99 days.
6. COVID-19 outpatients: early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low-dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study - Dec 2020 (published in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents)
Triple therapy for 5 consecutive days in addition to standard supportive care:- Zinc sulfate (220 mg capsule once daily, containing 50 mg elemental zinc);
- Hydroxychlroquine (200 mg twice daily); and
- Azithromycin (500 mg once daily).
Of 141 treated patients, 4 (2.8%) were hospitalised, which
was significantly fewer (P < 0.001) compared with 58
(15.4%) of 377 untreated patients.
One patient (0.7%) in the treatment group died versus 13
patients (3.4%) in the untreated group. No cardiac side
effects were observed.
Related:
Zelenko Protocol
7. Sabine Hazan - Effectiveness of Ivermectin-Based Multi-drug Therapy in Severe Hypoxic Ambulatory COVID-19 Patients - Jul 2021
Treatment was defined as ‘IVM Combination Therapy’ (ICT) and
consisted of ten days of oral:
- Ivermectin (12mg on day 1, day 4, and day 8)
- Doxycycline (100mg twice a day),
- Zinc (25mg twice a day),
- Vitamin D3 (1500 IU twice a day) and
- Vitamin C (1500mg twice a day). ICT was given daily for ten days only.
In 24 consecutive COVID-19 subjects with high risk features,
hypoxia and untreated moderate-severe symptoms averaging 9
days, we trialed this novel combination comprising
ivermectin, doxycycline, zinc, and Vitamins D and C. It was
highly effective. All subjects resolved symptoms in 11 days
on average, and oxygen saturation improved in 24hrs (87.4%
to 93.1%, p=0.001).
8. Mahmud (DB RCT) - Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial - May 2021
The treatment group received a single dose of ivermectin 12 mg
and doxycycline 100 mg, twice daily for 5 days, in addition to
standard of care. (n= 200)
The median recovery time was 7 days
The placebo group received placebo in addition to standard of care. (n=200)
Standard of care included administration of paracetamol,
antihistamines, cough suppressants, vitamins, oxygen therapy
according to indication and need, low molecular weight heparin
according to indication, appropriate other broad-spectrum
antibiotics, remdesivir injection, other antiviral drugs, and
other drugs for associated comorbid conditions.
9. Chechter et al., medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.11.05.21265569
(Preprint) - Nov 2021
Evaluation of patients treated by telemedicine in the COVID-19
pandemic by a private clinic in São Paulo, Brazil: A
non-randomized clinical trial preliminary study (n=187).
Adults: first day (attack phase) hydroxychloroquine sulfate 400
mg 12/12h; second to fifth day (maintenance phase) 200 mg (half
pill) 12/12h. The medication was associated with azithromycin
500mg once a day for five days.
For children with moderate symptoms were used:
hydroxychloroquine sulfate 6.5 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours in the
first day and 3.25 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours from day 2 to 5.
It was possible to observe in patients treated their symptoms
of COVID-19 (group 3) with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin
for five days, presented statistically better improvement of
the symptoms when compared to those that did not follow the
protocol (p = 0.039). Three patients were hospitalized and
discharged after recovery.
10. Seet et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.035 (Peer Reviewed) - Apr 2021
Positive impact of oral hydroxychloroquine and povidone-iodine throat spray for COVID-19 prophylaxis: an open-label randomized trialProphylaxis RCT in Singapore with 3,037 low risk patients, showing lower serious cases, lower symptomatic cases, and lower confirmed cases of COVID-19 with all treatments (ivermectin, Hydroxychloroquine, Povidone Iodine, and Zinc + vitamin C) compared to vitamin C.
There were no hospitalizations and no deaths.
11. Koshak et al., Complementary Therapies in Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2021.102769 (Peer Reviewed) - Aug 2021
Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19: An open-label randomized controlled clinical trial500mg Nigella sativa oil (MARNYS Cuminmar) twice daily for 10 days.
CUMINMAR: Manufactured by a Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) certified facility
Marnys® (Cartagena, Spain; brand name: CUMINMAR).
The standard of care was decided by the treating physicians and included antipyretics, antihistamines, and other drugs as per the Saudi Ministry of Health and the KAUH (King Abdulaziz University Hospital) protocol.
Risk of hospitalization: Treatment 1 of 91 (1.1%), Control 4 of 92 (4.3%).
Risk of hospitalization: Treatment 1 of 91 (1.1%), Control 4 of 92 (4.3%).
12. Hasan et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.10.012 (Peer Reviewed) - Oct 2021
The Effect of Melatonin on Thrombosis, Sepsis and Mortality Rate in COVID-19 Patients
All of the intervention group patients received standard therapy
plus 10 mg melatonin (Natrol®) once daily 20-30 minutes before
bed time for 14 days following diagnosis.
Risk of death, 92.9% lower, RR 0.07, p < 0.001, treatment 1 of 82 (1.2%), control 13 of 76 (17.1%).
Risk of death, 92.9% lower, RR 0.07, p < 0.001, treatment 1 of 82 (1.2%), control 13 of 76 (17.1%).
13. Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation Against Early-Stage COVID-19 Infection: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, and Open-Label Study - June 2021
152 COVID-19 outpatients a daily dose of 400 mg of quercetin
for 30 days to evaluate its adjuvant effects in the treatment
of early symptoms and the prevention of severe infection.
According to the authors:
“The results revealed a reduction in frequency and length of hospitalization, in need of non-invasive oxygen therapy, in progression to intensive care units and in number of deaths. The results also confirmed the very high safety profile of quercetin and suggested possible anti-fatigue and pro-appetite properties.
QP (Quercetin Phytosome®) is a safe agent and in combination with standard care, when used in early stage of viral infection, could aid in improving the early symptoms and help in preventing the severity of COVID-19 disease. It is suggested that a double-blind, placebo-controlled study should be urgently carried out to confirm the results of our study.”
“The results revealed a reduction in frequency and length of hospitalization, in need of non-invasive oxygen therapy, in progression to intensive care units and in number of deaths. The results also confirmed the very high safety profile of quercetin and suggested possible anti-fatigue and pro-appetite properties.
QP (Quercetin Phytosome®) is a safe agent and in combination with standard care, when used in early stage of viral infection, could aid in improving the early symptoms and help in preventing the severity of COVID-19 disease. It is suggested that a double-blind, placebo-controlled study should be urgently carried out to confirm the results of our study.”
The Quercetin group were prescribed, along with the same
standard care as for the control group, with an adjunctive daily
supplementation, lasting 30 days, constituted by 2 tablets/day
(1 every 12 hours) containing quercetin formulated with
sunflower lecithin in a 1:1 weight ratio. Each tablet (Quevir®,
a dietary supplement notified by Pharmextracta S.p.A., Italy,
contained 500 mg of Quercetin Phytosome® (QP) developed by
Indena S.p.A., Milan, Italy. QP corresponded to 200 mg of
quercetin; therefore, each daily treatment corresponded to 400
mg of quercetin.
14. Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19) - Nov 2020
A study published in November 2020 from Singapore (CW Tan, Nutrition 2020), found that those who were started on a daily oral dose of
vitamin D3 (1,000 IU), magnesium (150 mg) and vitamin B12 (500
mcg) within the first day of hospitalization and continued up
to 14 days were significantly less likely to require oxygen
therapy and further intensive care.
15. Ashraf et al. Honey and Nigella sativa against COVID-19 in Pakistan (HNS-COVID-PK): A multi-center placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial - Nov 2020
Three hundred and thirteen patients - 210 moderate and 103 severe
- underwent randomization from April 30 to July 29, 2020.
Among these, 107 were assigned to HNS (Honey plus Nigella Sativa)
whereas 103 to placebo for moderate cases.
For severe cases, 50 were given HNS and 53 were given
placebos.
HNS resulted in ∼50% reduction in time taken to alleviate symptoms
as compared to placebo (Moderate (4 versus 7 days), Hazard Ratio
[HR]: 6.11; 95% Confidence Interval [CI]: 4.23-8.84, P<0.0001
and severe (6 versus 13 days) HR: 4.04; 95% CI, 2.46-6.64,
P<0.0001).
HNS further led to a better clinical score on day 6 with normal activity resumption in 63.6% versus 10.9% among moderate cases (OR: 0.07; 95% CI: 0.03-0.13, P<0.0001) and hospital discharge in 50% versus 2.8% in severe cases (OR: 0.03; 95% CI: 0.01-0.09, P<0.0001).
In severe cases, mortality rate was four-fold lower in HNS group than placebo (4% versus 18.87%, OR: 0.18; 95% CI: 0.02-0.92, P=0.029).
No HNS-related adverse effects were observed.
What's New
Check out this highly navigable website that has continuously
updated the evidence-based research on early COVID-19 treatments
since June 2020: C19Early.com.
.png)

.png)



.png)


Comments
Post a Comment