Best Foods for Stem Cell Regeneration 2024
Stem Cells Develop Into All Cells, Renew Organs
We develop from stem cells. When the father’s sperm meets the mother’s egg, a fertilized egg is formed. It continues to divide and by day three to five develops into an embryo consisting of about 150 stem cells in the mother’s uterus. Later, these stem cells in the embryo continue to split and form various tissues and organs in the human body. There are more than two hundred different kinds of cells in the human body, all of which grow from stem cells. (Mayo Clinic)Stem cells are not only present at the embryonic development stage. When babies are born, they carry a large number of stem cells within their bodies. The average person has about 37.2 trillion cells, including about 750 million stem cells, which account for 0.002 percent of the total cells (Page 27, Eat to Beat Disease). These stem cells are stored in various parts of the body, ready to regenerate or repair body tissues and organs.
Dr. William Li, the author of “Eat to Beat Disease,” president of the Angiogenesis Foundation and a Harvard-trained medical doctor, elaborated on the role of stem cells in an interview with The Epoch Times. Li said stem cells are mainly stored in the bone marrow, though also found in the body’s fat, skin, hair follicles, and even in the heart. He made an analogy: The human body retains and dispatches stem cells just like we keep unused paint in the garage during renovation, which is ready for use if necessary, say, for wall repair someday.
As all human tissues and organs get renewed constantly, stem cells play a key role in this process. Specifically, we need them to produce new skin to replace damaged skin cells; and to replace damaged cells on the surface of the intestine. Besides, hematopoietic stem cells divide and replace those blood cells that are damaged while operating in the circulatory system. They, too, evolve into types of white and red blood cells, and more.
Interestingly, our small intestine is renewed every two to four days; our lungs and stomach every eight days; our skin every two weeks; our red blood cells every four months; our fat cells every eight years; and our skeleton every ten years. Dr. Li cited an example: The body’s immune cells regenerate every seven days. Therefore, if a person’s relevant stem cells disappear, he or she could die soon from an infection (Page 26, “Eat to Beat Disease”).
In addition, he quoted a Japanese story of nuclear radiation to highlight the critical life-supporting role of stem cells in his book. During the Second World War, the atomic bombardments in the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki caused about 200,000 deaths. Afterward, a second wave of deaths hit certain survivors because the ability of their bone marrow to make stem cells had been destroyed due to exposure to radiation. Further, in cancer treatment, chemotherapy and radiotherapy affect the survival of stem cells while destroying cancer cells, putting patients in tremendous pain and challenges (page 26, “Eat to Beat Disease“).
Related: Best Stem Cell Supplements
Stem Cells Repair Human Body in Times of Danger
The human body is born with mechanisms that collaborate seamlessly and automatically to keep life going.Stem cells come into play when we need to repair cells that are damaged due to various diseases and injuries or replace dysfunctional cells. Figuratively, stem cells are sentinels in the body that are always watching out for health needs and will at times appear at designated locations in preparation for rescue operations.
Dr. Li added that a damaged organ or site in need of repair releases a certain protein that acts as a messenger, calling on stem cells stored in the bone marrow. Then, the cells will respond to the call by leaving the bone marrow and entering the bloodstream. This scenario is almost like a group of bees swarming out of their hive. Together with the blood, stem cells flow to the injured tissue and land at their precise destination. Upon arriving, they begin to divide or transform themselves to regenerate organ or tissue cells.
As is well known, the liver is regenerative. It is the repair and regeneration function of stem cells that explains exactly why the liver can grow back into its original status, even if up to 75 percent of it is removed during surgery.
Likewise, our heart depends on stem cells to keep regenerating constantly, though the rebirth rate is affected by age. A 20-year-old gets about one percent of his or her heart cells renewed every year. However, this rate slows down as he or she gets older. At 75, that person gets only 0.3 percent of the heart cells renewed each year.
Reading that, you may wonder: Will stem cells eventually be depleted as they keep flowing out of the bone marrow? Dr. Li’s answer is, “Stem cells are capable of regenerating themselves and replenishing their stores in the bone marrow.”Excess of Glucose in Bloodstream Damages Stem Cells
1. Smoking and inhalation of air pollutants
When smokers inhale cigarette smoke, that leads to a lack of oxygen in the body, which will recruit stem cells into the bloodstream. Habitual smoking keeps consuming the stem cells stored in the bone marrow. A study has shown that the remaining stem cells in smokers’ bodies have a 75 percent drop in their self-reproduction ability and a 38 percent reduction in their involvement in regeneration. Besides active smoking, Dr. Li added, passive inhalation of secondhand smoke and exposure to heavily polluted air can be equally harmful to stem cells.
2. Excessive drinking
Addiction to alcohol kills stem cells. Like smoking, drinking alcohol causes stem cells to be constantly pulled out of the bone marrow into the circulatory system. Meanwhile, stem cells become damaged, negatively affecting their regeneration abilities, according to Dr, Li. Furthermore, drinking alcohol impairs the activity of stem cells in the brain, which in turn affects the hippocampus—responsible for short- and long-term memory.
3. Hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia
Both hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia impair stem cells. Dr. Li says in his book that bad cholesterol in the blood, known as low-density lipoprotein (LDL), damages liver cells while good cholesterol, known as high-density lipoprotein (HDL), delays the death of endothelial progenitor cells—a type of stem cell in the blood that maintains the health of blood vessels and repairs their inner layers.
Additionally, diabetes is a stem cell killer. Diabetics are likely to have 47 percent fewer stem cells than normal, with the remaining part of stem cells unable to function properly. This is because hyperglycemia affects stem cell replication and migration, as well as the secretion of survival factors.
Dr. Li also mentioned that high levels of stress and high salt levels in the blood also harm stem cells.
Eat the Right Foods to Increase Stem Cells in Your Body
Dr. Li gives advice on how to protect the activity of stem cells in the body and actively mobilize them to repair the body from a dietary perspective. Human experiments have confirmed the following foods, which can increase the number of stem cells.
1. Olive oil
PubMed has indexed 30 research studies on olive oil and stem cell.
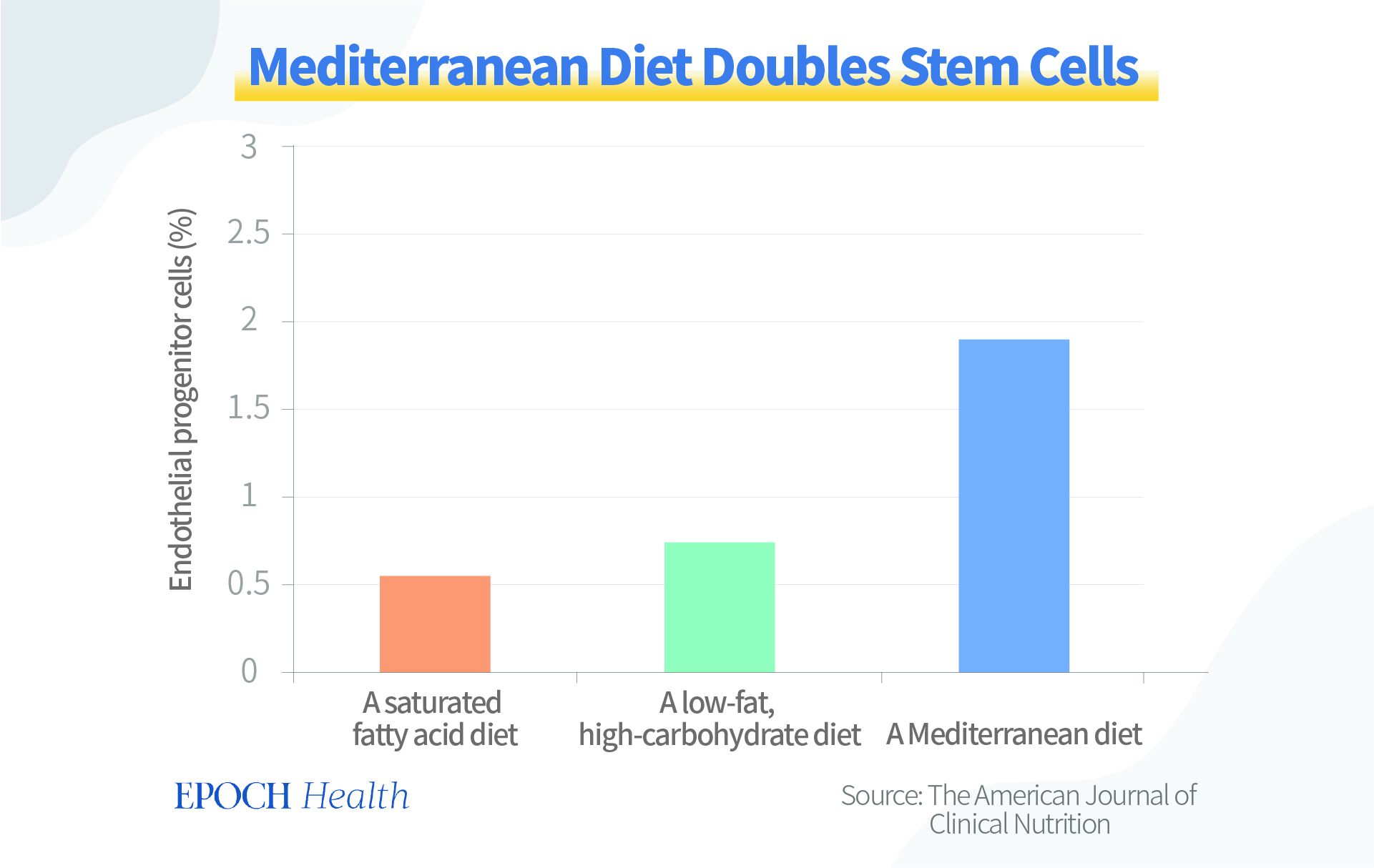
A Mediterranean diet rich in virgin olive oil is effective in boosting stem cells. A 4-week control study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2011) showed that compared to those on a diet high in saturated fat or a diet low in fat but high in carbohydrates, those on a Mediterranean diet rich in virgin olive oil showed a significant doubling in their endothelial progenitor cell count in the blood.
2. Dark chocolate
Dark chocolate contains flavanols that have biological properties. Researchers at the University of California recruited patients with coronary artery disease in a 30-day controlled trial. One group drank hot chocolate low in flavanols (only nine mg per serving) twice a day, and the other group drank hot chocolate high in flavanols (containing 375 mg per serving) twice a day. The results were surprising: the group with high-level flavanol had twice as many stem cells in their blood as that with low-level flavanol, and the former’s blood flow improved twice as much as the latter.
3. Black tea
A team of Italian researchers divided patients who had mild to moderate hypertension but did not receive medication into two groups. Group A drank plain black tea without sugar and milk twice a day while group B drank other beverages twice a day. One week later, blood tests showed the number of endothelial progenitor cells in the blood in the black-tea group rose by 56 percent, with an improved ability of blood vessel widening.
Updated and Republished from: https://www.theepochtimes.com/health/eat-the-right-foods-to-boost-your-stem-cells_4885749.html
Related:
.png)

.png)



.png)


To find a stem cell therapy provider in Asia, check out Stem Cell Therapy Asia
ReplyDelete